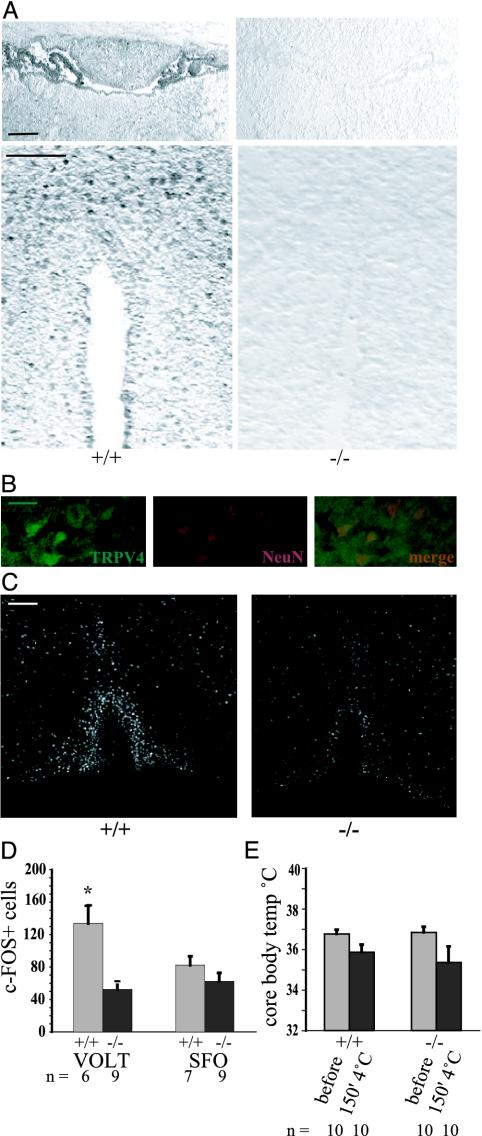
Fig. 4.
Specific impairment of CNS sensing of systemic osmotic pressure in trpv4-/- mice. (A) Immunohistochemistry for TRPV4 in the lamina terminalis. (Upper) Depicted is the circumventricular organ, SFO, and adjacent to it is the choroid plexus. The SFO is prominent in the rostral part of the third ventricle and is located caudally to the ventral hippocampal commissure. Note the absence of specific staining in the nulls. (Lower) Depicted is the circumventricular organ, the OVLT. The rostral portion of the anterior end of the third ventricle is sectioned; note specific staining in the OVLT in wild-type littermate mice, but not in trpv4-null mice. (Bar, 50 μm.) (B) Colabeling of TRPV4+ cells in the OVLT (Left, green fluorescence) with neuronal marker NeuN (Center, red fluorescence). Merged images are on the right. (Bar, 10 μm.) (C) Micrograph of the circumventricular organ, the OVLT, in the lamina terminalis. Shown here is immunohistochemistry for the c-FOS immediate early response gene. Representative micrographs of the lamina terminalis in a trpv4-/- mouse and in a wild-type littermate control mouse are shown. Note activation of the OVLT (inverted-U shape) and the rostrally positioned median preoptic area, MnPO. Mice were injected i.p. with 0.5 M NaCl, and their brains were fixated in formalin 90 min later. (Bar, 50 μm.) (D) Morphometry of c-FOS+ cells in circumventricular organs, the OVLT and the SFO. A significantly lower count of cells was noted in the OVLT of trpv4-/- mice, whereas the lower count in the SFO did not reach statistical significance. (E) Response to cold stress. Core body temperature was recorded by a rectal probe at 0 and 150 min. Mice were single-housed without food and water and exposed to 4°C for 150 min. Core body temperature dropped <36°C in both genotypes. Mean body temperature after the cold stress test was slightly lower in trpv4-/- mice, but the difference did not reach statistical significance.