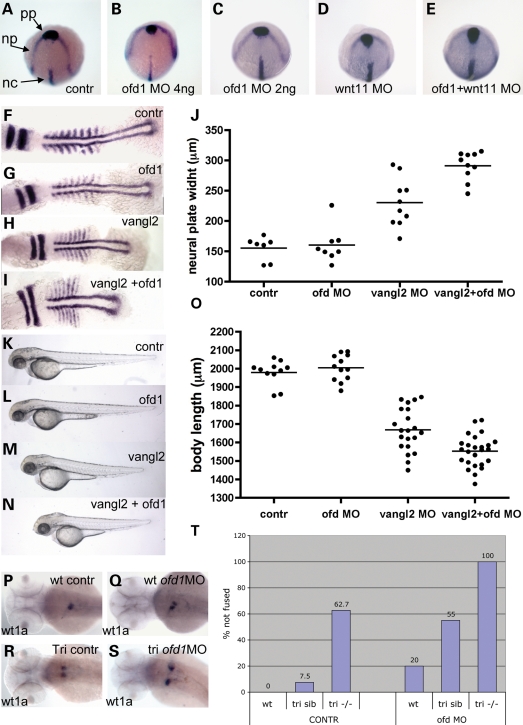
Figure 6.
CE failure in ofd1 MO-injected embryos. (A–E) Tailbud stage embryos hybridized with a cocktail of riboprobes: hgg1 as a marker for prechordal plate (pp), dlx3 as a marker for anterior margin of the neural plate (np) and ntl as a notochord (nc) marker. pp migration was delayed and the neural plate was wider in some embryos injected with 4 ng ofd1 SPL6 MO (B), but not in those injected with 2 ng only (C). Similar CE defects were observed in a subset of wnt11 MO-injected embryos (D), while all embryos showed the defects upon co-injection (E). (F–I) Embryos at the seven-somite stage hybridized with riboprobes for myoD, a marker of somite and adaxial cells, and krox20, a marker for rhombomeres 3 and 5. Representative embryos are shown: control (F), injected with ofd1 SLP MO (G), injected with vangl2 MO (H) and co-injected (I), with neural plate widths shown in (J). Note that co-injection of low dose ofd1 MO with vangl2 MO accentuated rhombomere widening and axis shortening versus vangl2 MO-injected embryos (see Results text for details). (K–O) When assessed at 60 hpf, ofd1 and vangl2 MO co-injected embryos had shorter bodies than those injected with vanlg2 MO alone (see Results text for details). (P–S) wt1a ISH to detect glomeruli at 60 hpf. Note the fused glomerulus in controls (P), with examples of failed fusion in wild-type embryos injected with ofd1 SPL6 MO (4 ng) (Q), tri mutants without (R) or with (S) ofd1 SP6 MO (4 ng); note the extreme separation of glomeruli in the latter condition. (T) Frequencies of failed fusion: note the accentuation of failed fusion in tri siblings upon injection of ofd1 MO.