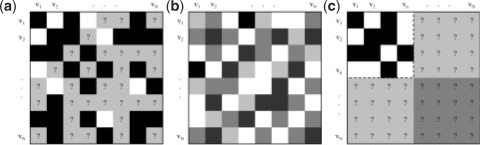
Fig. 1.
The supervised network inference problem. (a) Adjacency matrix of known interactions (black boxes), known non-interactions (white boxes) and node pairs with an unknown interaction status (gray boxes with question marks). (b) Kernel matrix, with a darker color representing a larger inner product. (c) Partially complete adjacency matrix required by the supervised direct approach methods, with complete knowledge of a submatrix. In the basic local modeling approach, the dark gray portion cannot be predicted.