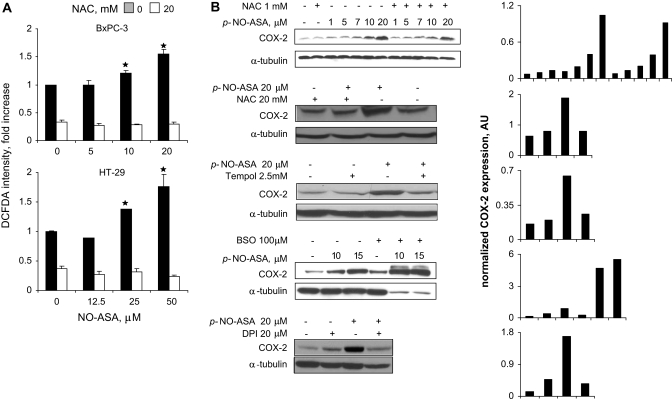
Fig. 3.
NO-ASA induces ROS and COX-2 in pancreatic cancer cells. (A) BxPC-3 and HT-29 cells were treated with one of three concentrations of p-NO-ASA for 3 h. ROS levels were detected by using the general probe DCFDA as in Materials and Methods (30 min staining). Four hours pretreatment with NAC 10 mM abrogated the induction of ROS. (B) BxPC-3 cells were treated with three antioxidants (NAC for 24 h, Tempol for 24 h and diphenylene iodonium for 2 h) or BSO, the inhibitor of glutathione biosynthesis, for 24 h prior to 4 h treatment with p-NO-ASA. COX-2 expression was detected by immunoblotting of total cell protein lysates. While the levels of α-tubulin used as a loading control were markedly reduced in response to the combined treatment with BSO and NO-ASA; Ponceau S staining of the same immunoblot membrane revealed equal protein loading (data not shown). Each lane has been quantified by densitometry and values have been normalized to the corresponding α-tubulin (loading control). The results for each immunoblot are shown in the last column; numbers in the abscissa represent the corresponding immunoblot lanes. *P<0.01 compare to control untreated cells.