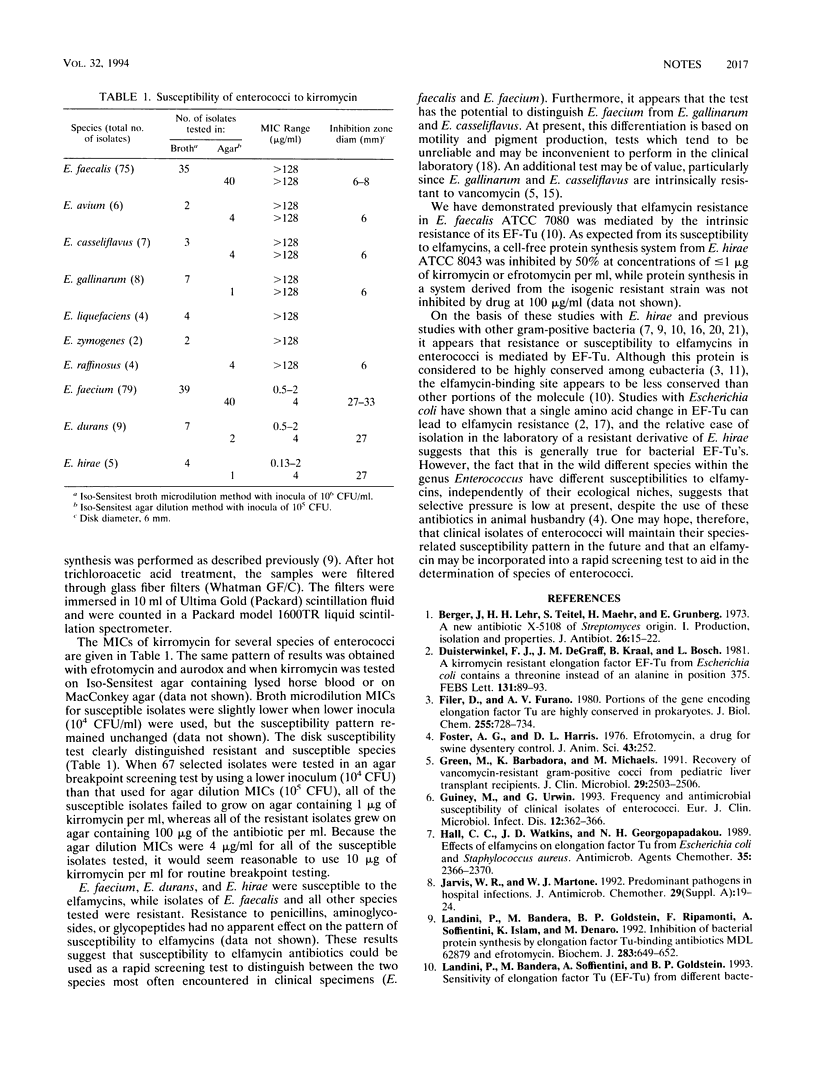
Abstract
The elfamycins are a class of naturally occurring antibiotics not currently used in the therapy of human disease. Enterococcus faecium and closely related species (Enterococcus durans and Enterococcus hirae) are susceptible to these antibiotics, while isolates of Enterococcus faecalis and other enterococcal species are highly resistant. Among enterococci, susceptibility or resistance to elfamycins appears to be determined by the bacterial protein synthesis elongation factor EF-Tu. Elfamycin susceptibility may be a useful adjunct for rapidly distinguishing E. faecalis and E. faecium in the clinical microbiology laboratory and/or as a supplementary test for use in determining the species of enterococci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J., Lehr H., Teitel S., Maehr H., Grunberg E. A new antibiotic X-5108 OF Streptomyces origin. I. Production, isolation and properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Jan;26(1):15–22. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., de Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L. A kirromycin resistant elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli contains a threonine instead of an alanine residue in position 375. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 17;131(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filer D., Furano A. V. Portions of the gene encoding elongation factor Tu are highly conserved in prokaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):728–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Barbadora K., Michaels M. Recovery of vancomycin-resistant gram-positive cocci from pediatric liver transplant recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2503–2506. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2503-2506.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiney M., Urwin G. Frequency and antimicrobial susceptibility of clinical isolates of enterococci. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 May;12(5):362–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01964435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. C., Watkins J. D., Georgopapadakou N. H. Comparison of the Tu elongation factors from Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli: possible basis for elfamycin insensitivity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2366–2370. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis W. R., Martone W. J. Predominant pathogens in hospital infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Apr;29 (Suppl A):19–24. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.suppl_a.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini P., Bandera M., Goldstein B. P., Ripamonti F., Soffientini A., Islam K., Denaro M. Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by elongation-factor-Tu-binding antibiotics MDL 62,879 and efrotomycin. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):649–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2830649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Weizenegger M., Betzl D., Leidel E., Lenz T., Ludvigsen A., Möllenhoff D., Wenzig P., Schleifer K. H. Complete nucleotide sequences of seven eubacterial genes coding for the elongation factor Tu: functional, structural and phylogenetic evaluations. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00249075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. The life and times of the Enterococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):46–65. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., de la Maza L., Murtagh M. J., Spargo J. D., Ferraro M. J. Species identities of enterococci isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):435–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.435-437.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selva E., Beretta G., Montanini N., Saddler G. S., Gastaldo L., Ferrari P., Lorenzetti R., Landini P., Ripamonti F., Goldstein B. P. Antibiotic GE2270 a: a novel inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. I. Isolation and characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1991 Jul;44(7):693–701. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.44.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Etter L., Gutmann L. Synergistic killing of vancomycin-resistant enterococci of classes A, B, and C by combinations of vancomycin, penicillin, and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):776–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I., Paress P. Genetic and biochemical characterization of kirromycin resistance mutations in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1107-1117.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Effects of the mutation glycine-222----aspartic acid on the functions of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):2047–2054. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S., Knight R. G., Green M., Sahm D. F., Shlaes D. M. Vancomycin susceptibility and identification of motile enterococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2335–2337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2335-2337.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wörner W., Wolf H. Kirromycin-resistant elongation factor Tu from wild-type of Lactobacillus brevis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 20;146(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


