Figure 1.
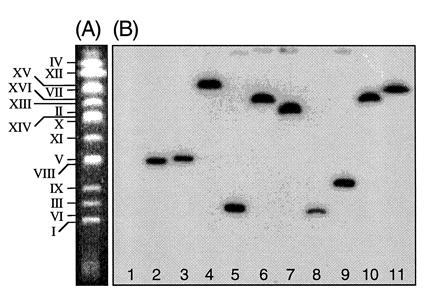
Integration of nonhomologous T-DNA into the genome of S. cerevisiae is random at the chromosome level. (A) A CHEF gel showing the separated chromosomes of an untransformed colony of S. cerevisiae strain RSY12. Each chromosome is indicated. (B) Chromosomes from Ura+ strains obtained after cocultivation of LBA1126(pRAL7102) with RSY12 were separated on a CHEF gel and blotted to a nylon membrane. The blot was probed with a labeled 1.1-kb HindIII URA3 fragment. Lane 1, RSY12 (not cocultivated); lane 2, Ura+ S. cerevisiae M5-1a strain obtained after cocultivation of M5-1a with LBA1100(pRAL7100). The T-DNA has integrated via a double crossover on chromosome V (11). Lane 3, as in lane 2, but the whole binary vector pRAL7100 has integrated via a single crossover on chromosome V, causing a shift in chromosome V mobility. Lanes 4–11, RSY12 Ura+ strains obtained after cocultivation of RSY12 with LBA1126(pRAL7102).
