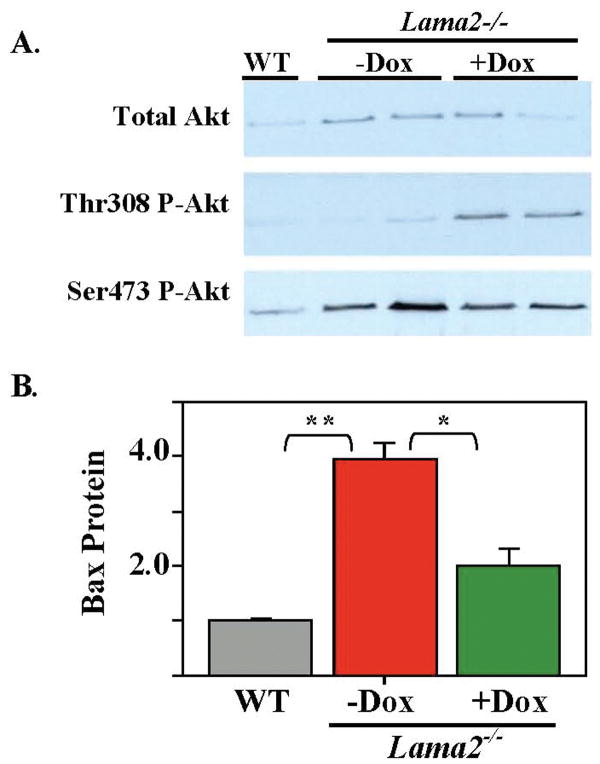
Fig. 7.
Doxycycline treatment increased phosphorylation of Thr308 on Akt and decreased expression of Bax in muscles of Lama2-/- mice. A. Leg muscles were obtained from a wild-type (WT) mouse, as well as two untreated Lama2-/- (-Dox) and two doxycycline-treated Lama2-/- (+Dox) mice; and muscle extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for total Akt, phosphoThr308-Akt, and phosphoSer473-Akt as indicated. Diseased muscles had more total Akt and more phosphoSer473-Akt than wild-type muscles, and doxycycline treatment increased the amount of phosphoThr308-Akt in Lama2-/- muscles. Equal amounts of total muscle protein were analyzed for each group (10 μg for total Akt, 125 μg for phosphorylated Akt forms) and equal loading was verified by GAPDH staining (not shown). B. Quantitative immunoblots showed that Bax protein was more abundant in muscles obtained from untreated Lama2-/- mice than in muscles from healthy wild-type mice and that doxycycline treatment lowered the amount of Bax protein in Lama2-/- muscles to nearer the wild-type level. Equal amounts of protein (50 μg) were analyzed for each sample, and equal loading was verified by immunoblotting for GAPDH (not shown). Relative amounts of Bax are plotted with the Bax/GAPDH ratio for wild-type set equal to one. Errors bars = SE; n=3. **P<0.01. * P<0.02.