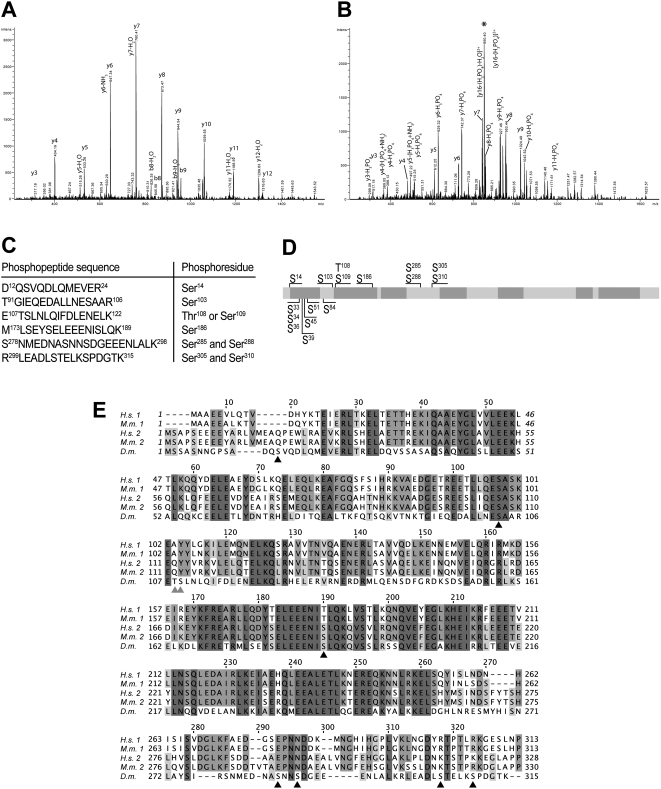
Figure 1. Location of BicD phosphorylation sites.
A, B: MS/MS spectra of the [M+2H]2+ ions of the peptide T91GIEQEDALLNESAAR106 (A) and its serine phosphorylated form (B). The intense, neutral loss fragment at m/z = 850.4 (marked with an asterisk) in B indicates the extensive loss of phosphoric acid. Upon collision induced fragmentation in the iontrap, peptide bond fragmentation allowed unambiguous characterization of the amino acid sequence and the presence of a phosphorylated Ser. Note the m/z shift of 80 mass units corresponding to the phosphorylation of serine at y(4) and following y- ions between A and B. Furthermore, y-ions showed also extensive loss of phosphoric acid corresponding to a y-ion series with 98 mass units difference in the same MS/MS spectrum in B. C: Summary of phosphopeptides and phosphorylation sites of BicD identified by MS analysis. Phosphorylation of Ser285 was only observed when Ser288 was phosphorylated as well. Of Ser305 and Ser310, both, single and double phosphorylations, were found. The peptide 12–24 is an incomplete tryptic fragment, whereas the shown peptide 299–315 has two missed cleavage sites. Due to its small size, the peptide S310PDGTK315 could not be identified individually. D: Schematic drawing of the BicD protein. The positions of phosphoserines identified by MS analysis are indicated on top. Additional mutants created for this study are indicated at the bottom. Coiled-coil domains were predicted using the program MARCOIL [43], and are shaded in dark grey (probability ≥90%). Drawing is to scale. E: Amino acid alignment of the BicD N-terminal part. The sequences of human BicD1 and 2 (H.s. 1, H.s. 2; SwissProt entries Q96G01 and Q8TD16, respectively), mouse BicD1 and 2 (M.m. 1, M.m. 2; Q8BR07, Q921C5) and Drosophila BicD (D.m.; P16568) were aligned using the program T-COFFEE [44]. Phosphorylated serines in Drosophila BicD are marked by black triangles, ambiguous sites are indicated by grey triangles.