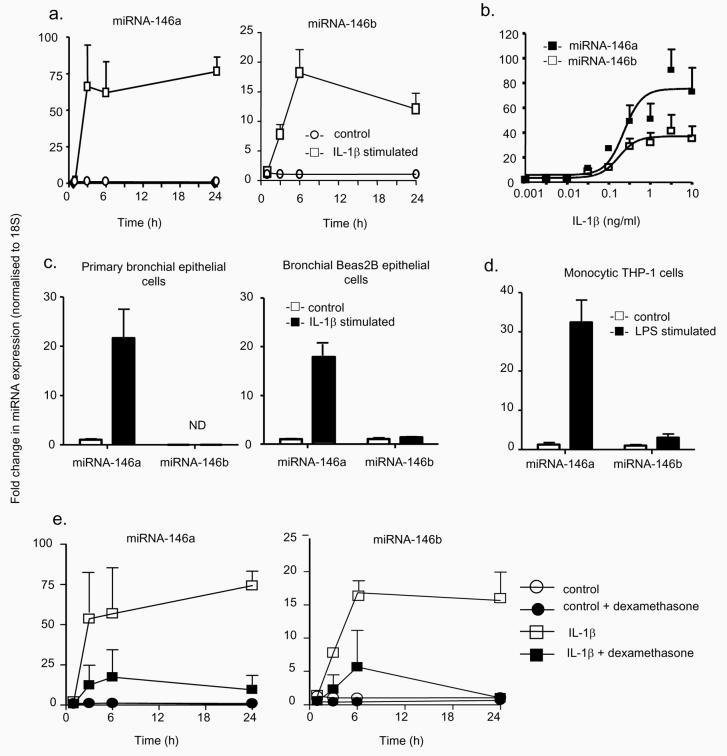
Figure 3.
Characterisation of the mechanism of miRNA-146a and miRNA-146b expression. The time- and concentration-dependent induction of miRNA-146a and miRNA-146b in A549 cells was determined following exposure to 1 ng/ml IL-1β for the indicated time (a) or to the indicated IL-1β concentration for 6 h (b) and the increases in miR-146a and miR-146b expression were determined by RT-PCR. To confirm the observations in A549 cells, the levels of miRNA-146a and miR-146b were measured at 6 h in IL-1β-stimulated primary human bronchial epithelial cells and transformed human bronchial Beas2B epithelial cells (c) or in LPS-stimulated monocytic THP-1 cells (d). Alternatively, control- and IL-1β-(1ng/ml) stimulated A549 cells were pre-treated with dexamethasone (1 μM) for 60 min, and the expression of miRNA-146a and miRNA-146b was determined at the indicated time points (e). These results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. ND = not detected.