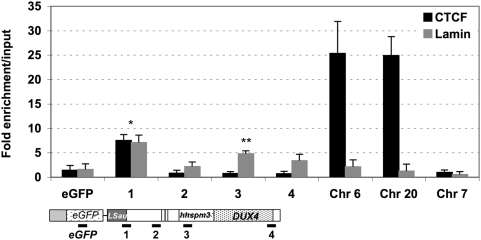
Figure 3. CTCF and A-type Lamins bind to D4Z4 in vivo.
We searched in silico for CTCF binding sites across the 3.3 kb D4Z4 sequence (Genbank accession number AF117653) using the consensus binding site at the chicken β-globin locus [22],[23]. Two sites were identified at the 5′ end of D4Z4 and the binding was investigated by ChIP using antibodies to CTCF. We also investigated the involvement of A-type Lamins using specific antibodies. Enrichment of the immunoprecipitated DNA fraction with antibodies compared to input DNA was determined after real-time Q-PCR amplification (y-axis) for different primer pairs. Values were normalized to the Histone H4 internal standard. Each bar is the average of at least three independent experiments with the S.D. shown by error bars. “eGFP” amplifies the eGFP sequence. The position of the primers within D4Z4 is indicated (sets 1–4). Using high-throughput analysis, numerous CTCF binding sites were recently identified and many of these sites also correspond to Cohesins enrichment [25]. We then asked if Cohesins/CTCF complex also contains A-Type Lamins and amplified DNA immunoprecipitated with Lamins A/C antibodies with primers corresponding to chromosome 6 (Chr 6). We observed a strong enrichment for CTCF but not Lamins at this site suggesting that CTCF/Cohesins and CTCF/Lamins bind distinct sites. A sequence on chromosome 20 (Chr 20) was reported as a site for CTCF only and does not bind A-type Lamins. Chr 7 primers are CTCF-negative control. Asterisks denote statistically significant values (** p<0.001; *p<0.005; Student's t test).