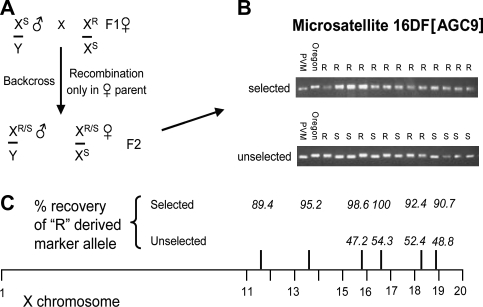
FIG. 3.
Recombination mapping between Oregon R 1970 and PVM using strain-specific microsatellite markers on the X chromosome to locate an arsenite tolerance/sensitivity locus. (A) Crossing scheme shows X-chromosomal constitution of F1 heterozygous females backcrossed to PVM males—recombination on the female X leads to male progeny that contain either the resistant (R) or the sensitive (S) arsenite-response allele. (B) Microsatellite mapping in the 16DF region of the X chromosome shows mobility difference depending on parental source (R or S), allowing genotypic frequency to be scored in F2 males either selected for survival on 1mM arsenite or not selected (i.e., raised on normal food). (C) “R”-derived allele frequencies were scored for a variety of markers located along the X chromosome. As expected, when not selected for arsenite resistance, markers segregated in an approximately 1:1 ratio. When the R allele approaches 100% representation in resistant males, very close linkage to the arsenite-responsive allele(s) is anticipated.