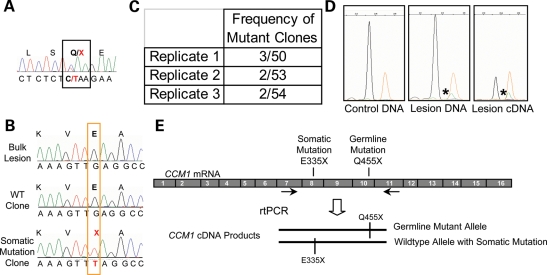
Figure 2.
A biallelic somatic mutation identified in CCM1 sample 2009. (A) Direct sequence analysis of bulk lesion-derived DNA identified the germline mutation as the common Hispanic mutation, CCM1 exon 10 c.1363C>T, Q455X. (B) Somatic mutation analysis identified a somatic mutation in CCM1 exon 8, c1003G>T, E335X. Direct sequence of lesion DNA shows only wild-type sequence. Sequence of individual clones reveals sequence for both wild-type clones and clones with the somatic mutation. (C) The somatic mutation was identified multiple times in each of the three rounds of PCR. Replicates 1 and 2 used HiFi Platinum Taq Polymerase (Invitrogen), and replicate 3 used HotStar Polymerase (Qiagen). (D) The somatic mutation is validated using the SNapShot Assay. The wild-type allele in blue (arrow) is present in all samples, whereas the somatic mutation in green (asterisk) is only present in the lesion-derived DNA or cDNA products and orange peaks are the size standard. Somatic mutant alleles represent ∼6% of the DNA-derived fragments and 24% of the cDNA-derived fragments analyzed. (E) The somatic and germline mutations are biallelic. RT–PCR products containing both somatic and germline mutant loci were amplified, cloned and sequenced. Sequencing analysis of individual colonies shows three classes of clones: germline mutant alleles, wild-type alleles and alleles carrying the somatic mutation that are wild-type for the germline mutation.