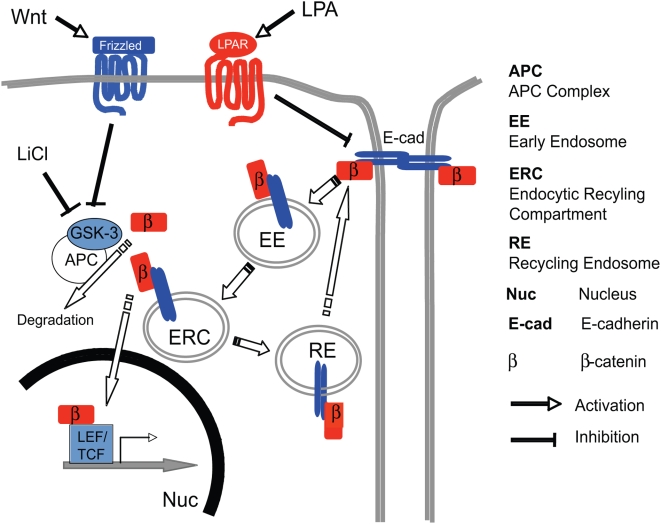
Figure 7. A schematic model for the intersection of cadherin-bound β-catenin pool with Wnt-signaling upon AJ dissociation by LPA stimulation.
ß-catenin (ß) is recruited to sites of cell-cell interactions and binds E-cadherin (E-cad) establishing adhesion via formation of adherens junctions (AJ). Upon LPA stimulation, AJ dissociate and cadherin-bound ß-catenin travels to the early endosome (EE), endocytic recycling compartment (ERC) [and potentially the recycling endosome (RE) before its exit back to AJ area], before being translocated into the nucleus (Nuc) of the cell, where it engages transcription factors such as TCF and LEF (altering gene expression). Translocation is dependent upon LiCl treatment or Wnt pathway activation (via binding to receptors encoded by frizzled genes), as these steps prevent glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK3ß) from phosphorylating the (APC) complex and ß-catenin substrate (ß). Unphosphorylated ß either degrades or escapes to the nucleus where it engages transcription factors such as TCF and LEF.