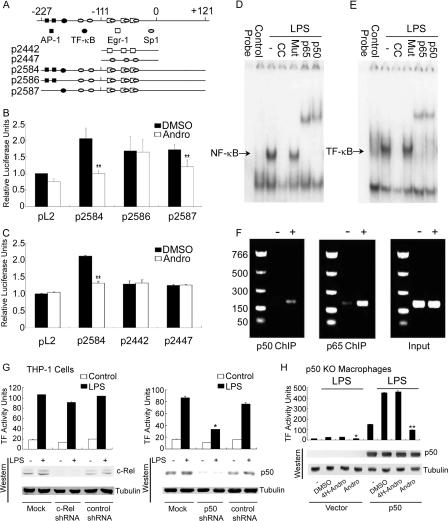
FIGURE 2.
Andro inhibits the promoter activity of the human TF gene and p50/p65 heterodimer binds to the TF-κB site. A, schematic description of the constructs of the human TF promoter. The plasmid of p2584 (-227 to +121) contains all the binding sites for AP-1, NF-κB, Sp1, and Egr-1 transcription factors. The plasmid of p2586 (-227 to +121) contains the AP-1, Sp1, and Egr-1 sites and a mutated NF-κB site. The plasmid of p2587 (-227 to +121) has the mutation of two AP-1 sites only. The plasmid of p2442 (-111 to +14) contains three Egr-1 sites, and the plasmid of p2447 (-111 to +14) contains the last three Sp1 sites. B, Andro targets the NF-κB site of the human TF promoter. THP-1 cells were transfected with plasmids of plain vector (pL2), p2584, p2586, and p2587 in the presence of DMSO and Andro. Transfectants were then incubated with TNF-α followed by measurements of luciferase activity using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega). C, Andro fails to antagonize the Egr-1 and Sp1 sites of the human TF promoter. THP-1 cells were transfected with the plasmids of pL2, p2584, p2442, and p2447 in the presence of DMSO and Andro. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements from three separate experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 versus DMSO group). D–F, the binding of p50/p65 heterodimer to the TF-κB site in the promoter of human TF. Radiolabeled NF-κB(D) and TF-κB(E) oligonucleotides were bound to nuclear proteins isolated from resting, LPS-stimulated HUVECs in the absence or presence of their unlabeled consensus and mutant oligonucleotide or anti-p50 and p65 Abs. Alternatively, ChIP was employed using anti-p50 and p65 Abs followed by PCR for amplification of TF promoter (F). G, p50 shRNA, but not c-Rel shRNA, attenuates TF activity. THP-1 cells were transfected with the plain vector (mock) or the plasmid of c-Rel shRNA, p50 shRNA, or non-inhibitory, control shRNAs and incubated with LPS for measurements of TF activity and immunoblotting. Results are presented as the mean ± S.D. value of triplicate measurements from three separate experiments. H, rescue of TF activity in p50-deficient macrophages and its inhibition by Andro. Macrophages isolated from p50 null mice were transfected with the plain vector or the plasmid of mouse p50 cDNA in the presence of DMSO, 4H-Andro, and Andro. They were then incubated with LPS for determination of TF activity and immunoblotting. Results are presented as the representative mean ± S.D. value of at least three separate experiments.