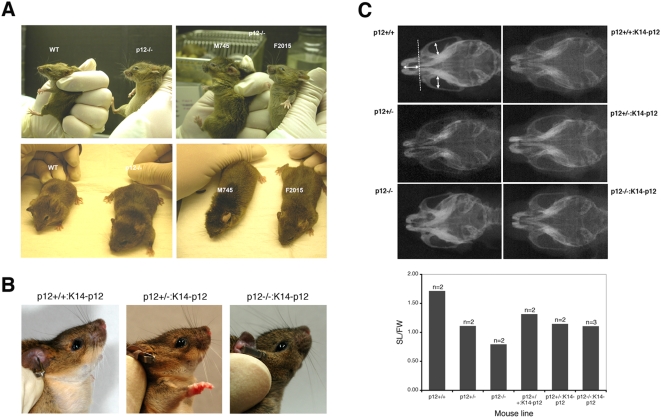
Figure 5. Craniofacial abnormality of survived Cdk2ap1−/− mice.
A. The craniofacial morphology was noticeably different between wild type (WT) and Cdk2ap1−/− mice. Two survived Cdk2ap1−/− mice (M745 and F2015) were also compared side-by-side and both mice showed similar craniofacial abnormality compared to WT. B. The complement expression of Cdk2ap1 in Cdk2ap1−/− mice by transgenic approach resulted in an increased incidence of homozygous Cdk2ap1 knockout mice. The rescued mice (Cdk2ap1−/−:K14-Cdk2ap1) also showed the recovery of the craniofacial deformity to the state of the heterozygous (Cdk2ap1+/−:K14-Cdk2ap1) mice. C. The craniofacial differences between animals were analyzed by measuring the Snout Length (SL) and Facial Width (FW) ratio measured on the X-ray films obtained in a standardized head position as indicated by the arrows. The average ratio was depicted and compared between Cdk2ap1+/+ and Cdk2ap1−/− mice, and also the hybrid animals with Cdk2ap1+/+:K14-Cdk2ap1, Cdk2ap1+/−:K14-Cdk2ap1, and Cdk2ap1−/−:K14-Cdk2ap1 genotype.