Abstract
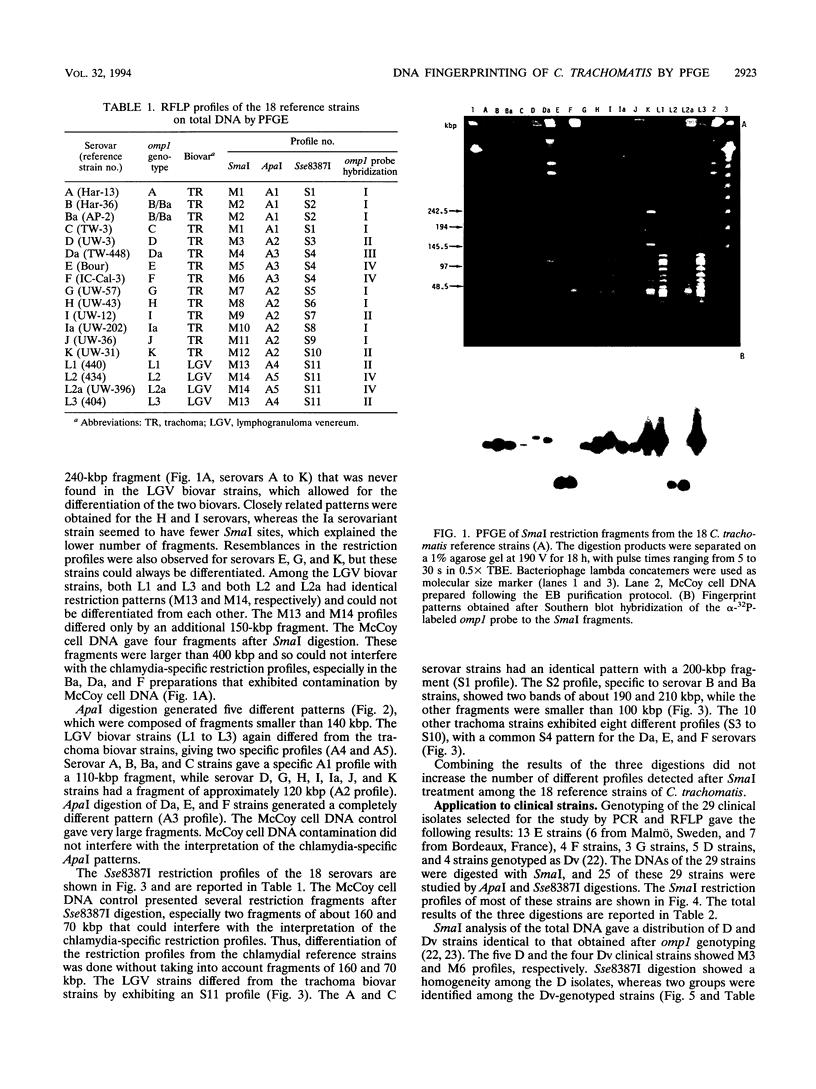
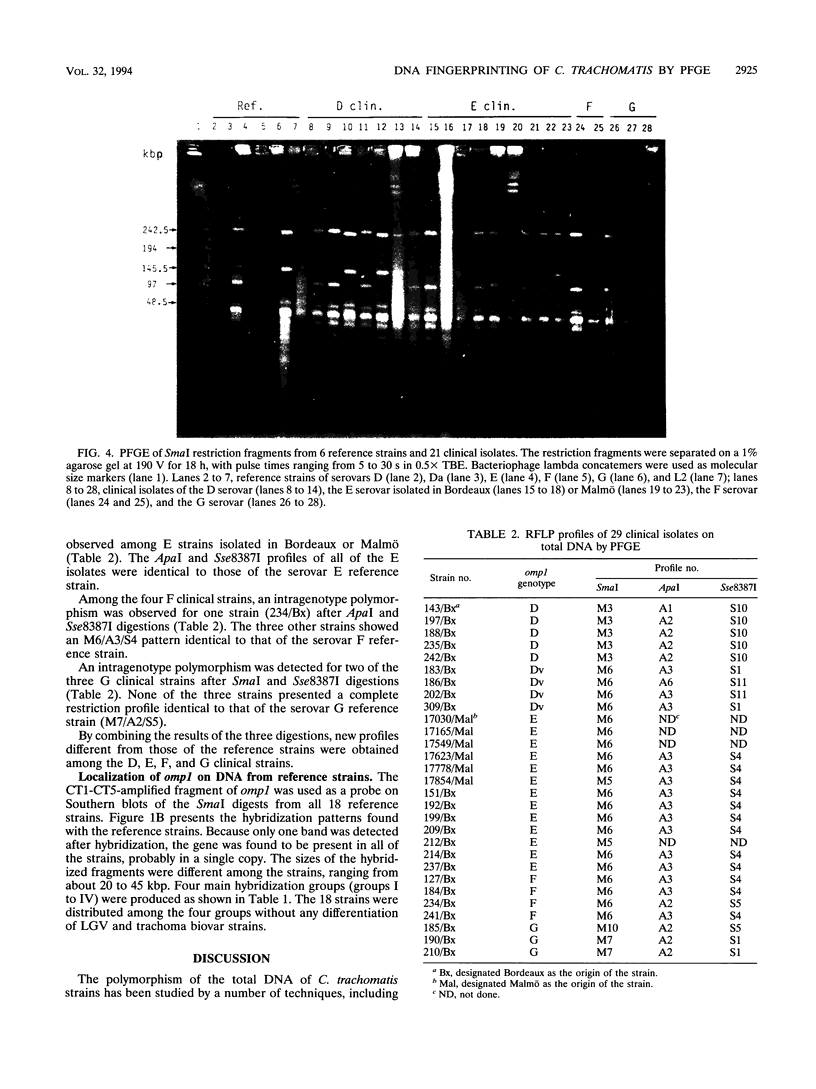
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) was applied to Chlamydia trachomatis reference strains representing each of the 18 serovars and to 29 clinical isolates from genital specimens collected in Bordeaux, France, or Malmö, Sweden. Comparison of the fingerprint patterns of the reference strains revealed a high level of polymorphism of the total DNA when SmaI was used (14 profiles), whereas the other enzymes, Sse8387I and ApaI, showed fewer differences. Some serovars, considered to be closely related on the basis of their antigenic determinants located on the major outer membrane protein (MOMP), such as D and Da or I and Ia, were shown to be different after PFGE of their genomic DNAs. However, serovars B and Ba and serovars L2 and L2a had identical patterns after analysis with the three endonucleases. When applied to clinical isolates, which were typed by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the MOMP gene, PFGE allowed the detection of intragenotype polymorphisms and showed the identity of two strains successively isolated from the same patient. This technique seems to be an efficient tool for epidemiological studies when used in addition to serotyping or genotyping by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the MOMP gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allardet-Servent A., Bouziges N., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bourg G., Gouby A., Ramuz M. Use of low-frequency-cleavage restriction endonucleases for DNA analysis in epidemiological investigations of nosocomial bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Sep;27(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.9.2057-2061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbeit R. D., Arthur M., Dunn R., Kim C., Selander R. K., Goldstein R. Resolution of recent evolutionary divergence among Escherichia coli from related lineages: the application of pulsed field electrophoresis to molecular epidemiology. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):230–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Stephens R. S. Construction of physical and genetic maps of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2742–2747. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2742-2747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukadida J., de Montalembert M., Gaillard J. L., Gobin J., Grimont F., Girault D., Véron M., Berche P. Outbreak of gut colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in immunocompromised children undergoing total digestive decontamination: analysis by pulsed-field electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2068–2071. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2068-2071.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carles-Nurit M. J., Christophle B., Broche S., Gouby A., Bouziges N., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphisms in methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2092–2096. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2092-2096.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carriere C., Allardet-Servent A., Bourg G., Audurier A., Ramuz M. DNA polymorphism in strains of Listeria monocytogenes. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1351–1355. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1351-1355.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D., Patton M., Stephens R. S. Direct sequence evaluation of the major outer membrane protein gene variant regions of Chlamydia trachomatis subtypes D', I', and L2'. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1579–1582. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1579-1582.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E. H., Deslandes S., Veilleux S., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. Typing Chlamydia trachomatis by detection of restriction fragment length polymorphism in the gene encoding the major outer membrane protein. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1103–1107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frutos R., Pages M., Bellis M., Roizes G., Bergoin M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis determination of the genome size of obligate intracellular bacteria belonging to the genera Chlamydia, Rickettsiella, and Porochlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4511–4513. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4511-4513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi H., Hirai K. Proposal of Chlamydia pecorum sp. nov. for Chlamydia strains derived from ruminants. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):306–308. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaydos C. A., Bobo L., Welsh L., Hook E. W., 3rd, Viscidi R., Quinn T. C. Gene typing of Chlamydia trachomatis by polymerase chain reaction and restriction endonuclease digestion. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Nov-Dec;19(6):303–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouby A., Carles-Nurit M. J., Bouziges N., Bourg G., Mesnard R., Bouvet P. J. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for investigation of hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1588–1591. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1588-1591.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of NotI digests of leptospiral DNA: a new rapid method of serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1696–1702. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1696-1702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltenboeck B., Kousoulas K. G., Storz J. Structures of and allelic diversity and relationships among the major outer membrane protein (ompA) genes of the four chlamydial species. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):487–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.487-502.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Weiss E. Lack of deoxyribonucleic acid homology between species of the genus Chlamydia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1421–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1421-1423.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Suchland R. J., Stamm W. E. Nucleotide sequence of the variable domains within the major outer membrane protein gene from serovariants of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):213–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.213-219.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. M., de la Maza L. M. Restriction endonuclease analysis of DNA from Chlamydia trachomatis biovars. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):625–629. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.625-629.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez P., Vekris A., de Barbeyrac B., Dutilh B., Bonnet J., Bebear C. Typing of Chlamydia trachomatis by restriction endonuclease analysis of the amplified major outer membrane protein gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1132-1136.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez P., de Barbeyrac B., Persson K., Dutilh B., Bebear C. Evaluation of molecular typing for epidemiological study of Chlamydia trachomatis genital infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2238–2240. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2238-2240.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayada C., Denamur E., Orfila J., Catalan F., Elion J. Rapid genotyping of the Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein by the polymerase chain reaction. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Sep 15;67(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90447-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayada C., Denamur E., Xerri B., Orfila J., Catalan F., Elion J. Epidémiologie de Chlamydia trachomatis par l'analyse du gène de la protéine majeure de membrane externe. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1992 May;40(5):583–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoonmaker D., Heimberger T., Birkhead G. Comparison of ribotyping and restriction enzyme analysis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for distinguishing Legionella pneumophila isolates obtained during a nosocomial outbreak. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1491–1498. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1491-1498.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scieux C., Grimont F., Regnault B., Bianchi A., Kowalski S., Grimont P. A. Molecular typing of Chlamydia trachomatis by random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Res Microbiol. 1993 Jun;144(5):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(93)90197-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scieux C., Grimont F., Regnault B., Grimont P. A. DNA fingerprinting of Chlamydia trachomatis by use of ribosomal RNA, oligonucleotide and randomly cloned DNA probes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Oct;143(8):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90103-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Three new serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis: Da, Ia, and L2a. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):403–405. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Barnes R. C., Stephens R. S., Grayston J. T. Immunotyping of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):791–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Zhang Y. X., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences for the four variable domains of the major outer membrane proteins of the 15 Chlamydia trachomatis serovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1040-1049.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]