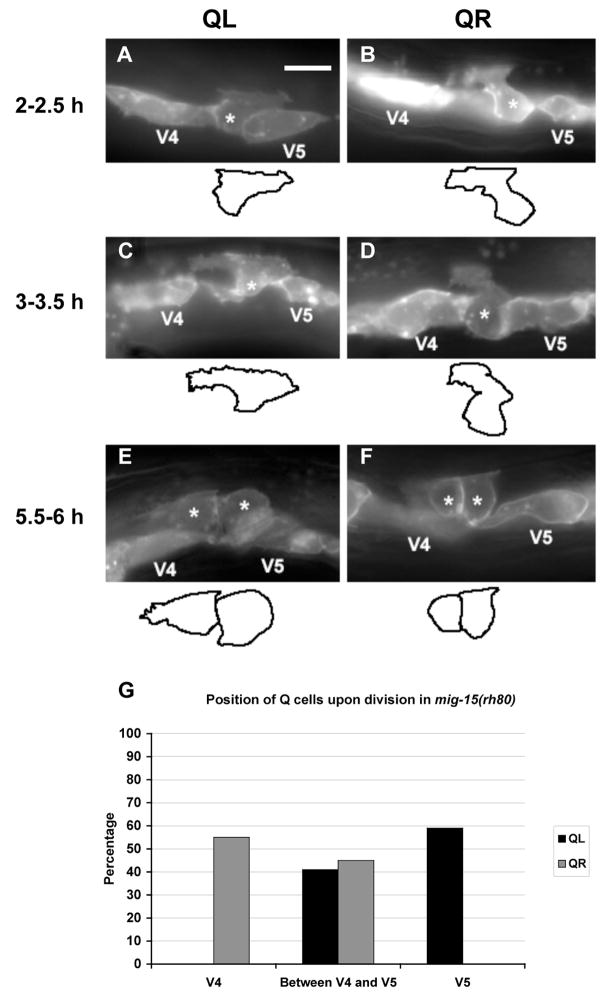
Figure 4. mig-15 NIK kinase strong loss-of-function mutation affects the polarizations and migrations of the Q neuroblasts.
(A–F) are panels of epifluorescent micrographs of Q neuroblasts of L1 larvae in mig-15(rh80) mutants with scm::gfp::caax expression. Asterisks mark the position of the Q neuroblast at 2–2.5 h after hatching (A–B) and 3–3.5 h after hatching (C–D) or Q neuroblast descendants at 5.5–6 h after hatching (E–F). Tracings of the Q neuroblasts found in each micrograph are located below each panel. The scale bar in (A) represents 5μm for (A–F). (A) A QL neuroblast polarized posteriorly over the V5L seam cell, but did not extend its protrusion nearly as far as in wild type. (B) A QR neuroblast polarized anteriorly over the V4R seam cell, but did not extend its protrusion nearly as far as in wild type. (C) A QL neuroblast sent protrusions in both anterior and posterior directions. (D) A QR neuroblast did not polarize strongly in either direction, although it sent a small protrusion anteriorly. (E) A QL neuroblast divided between the V4L and V5L seam cells. (F) A QR neuroblast divided between the V4R and V5R seam cells. (G) Quantitation of the position of the QL and QR neuroblasts upon division (5.5–6 h after hatching) in mig-15(rh80) mutants. The graph is organized as described in Figure 3K. For QL divisions, 41 animals were scored. For QR divisions, 38 animals were scored.