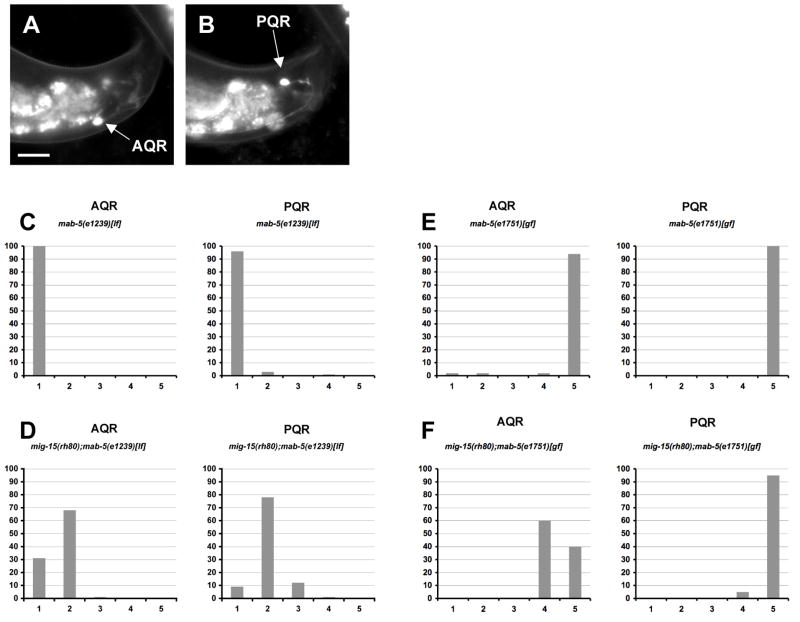
Figure 8. The AQR/PQR direction of migration defects seen in mig-15 NIK kinase hypomorphic mutants are dependent on MAB-5, whereas the failure to migrate defects are independent of MAB-5.
(A–B) are panels of epifluorescent micrographs of AQR and PQR neurons of a young adult in a mig-15(rh80) mutant with gcy-32::gfp expression. An AQR neuron (A) reversed the direction of migration and migrated to the tail of the animal near the PQR neuron (B). The scale bar in (A) represents 10μm for (A–B). (C–F) Quantitation of the final migratory positions of AQR and PQR. The graphs are organized as described in Figure 6D–F. mab-5(e1239)[lf] is a loss-of-function mutation, and mab-5(e1751)[gf] is a gain-of-function mutation. For each genotype, 100 animals were scored.