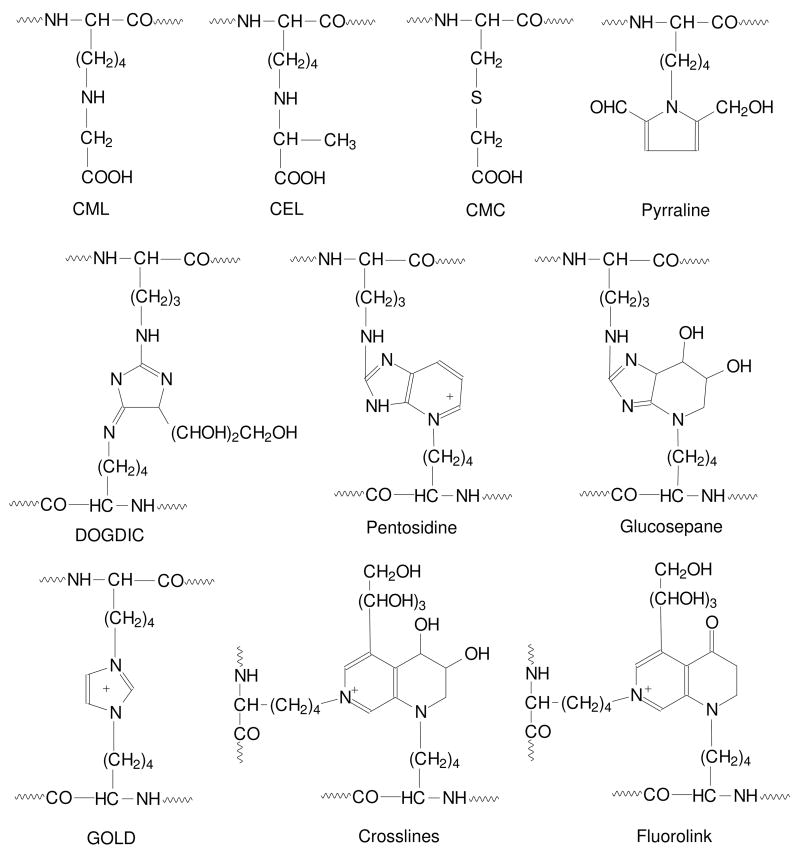
Figure 4. Representative advanced glycation end-products.
Oxidative decomposition of the Amadori product or reaction of tissue proteins with reactive carbonyl and dicarbonyl compounds can lead to the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). AGEs include Nε-(carboxymethyl)lysine (CML), Nε-(carboxylethyllysine) (CEL), S-(carboxymethyl)cysteine (CMC), pyrraline, 3-deoxyglucosone-derived imidazolium crosslink (DOGDIC), pentosidine, glucosepane, glyoxal lysine dimer (GOLD), crosslines, and fluorolink.