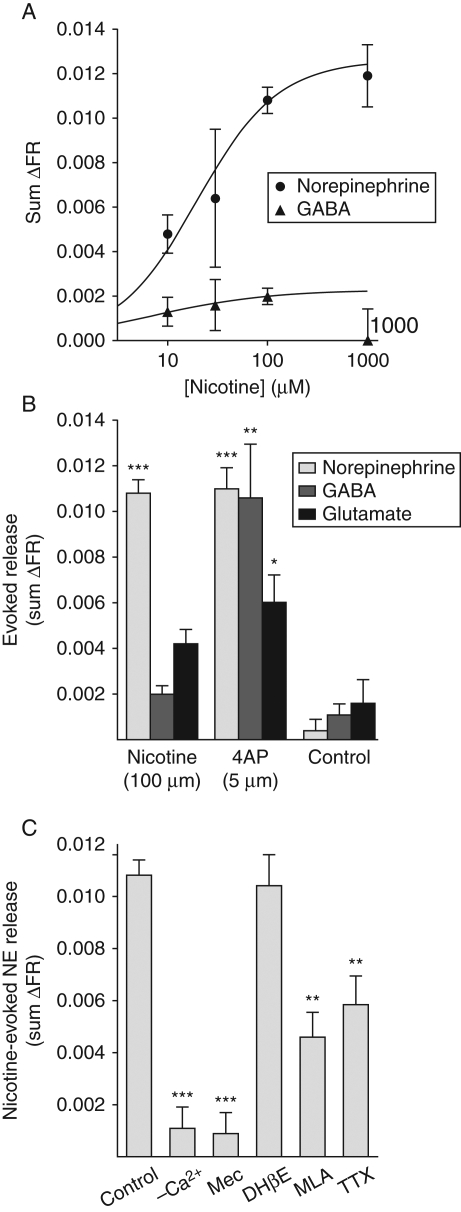
Fig 1.
Nicotine-evoked NE release from rat hippocampal nerve terminals. (a) Nicotine-evoked NE release (sum ΔFR) was concentration-dependent and transmitter-selective, and maximally stimulated by 100 µM nicotine (n=4). (b) Nicotine selectively evoked NE (n=61) compared with GABA (n=43) and glutamate (n=35) release, although all three transmitters were evoked by stimulation with 5 µM 4AP (n=13, 4, 17, respectively), which evoked fractional release of NE comparable with that evoked by nicotine. Statistical comparisons of sum ΔFR values [mean (sem)] were performed by one-way anova (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 vs control). (c) Nicotine-evoked NE release (n=61) required extracellular Ca2+ (n=8) and was nAChR-dependent as indicated by inhibition by the non-selective nAChR blocker mecamylamine (Mec, 10 µM, n=5). Release was not inhibited by the selective β2 antagonist DHβE (30 µM, n=5) and was partially inhibited by the selective α7 antagonist MLA (10 µM, n=8) or the Na+ channel blocker TTX (1 µM, n=12). Statistical comparison of sum ΔFR values [mean (sem)] with control was performed by one-way anova (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001).