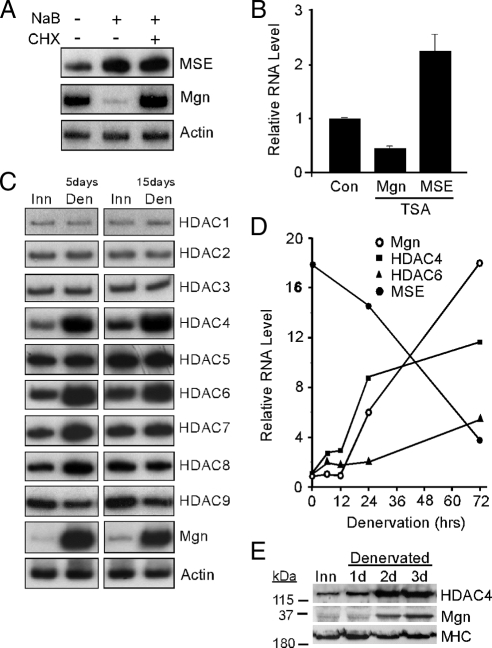
Figure 1.
Regulation of Mgn, MSE, and HDAC levels by HDAC inhibitors and muscle denervation. (A) Radioactive PCR showing MSE, Mgn, and γ-actin mRNA levels after treatment of differentiated C2C12 myotubes with the HDAC inhibitor NaB (5 mM) or vehicle (0.9% NaCl, 0.1% DMSO) for 6 h in the presence and absence of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX; 50 μg/ml). (B) Real-time PCR quantification of Mgn and MSE mRNA levels in denervated sternomastoid muscle that was bathed, in vivo, in the HDAC inhibitor TSA (5 μM) or vehicle (Con; 0.9% NaCl, 0.1% DMSO) for 12 h. Error bars are standard deviations, n = 3. (C) Radioactive PCR showing HDAC1-9, Mgn, and γ-actin mRNA levels in innervated (Inn), and 5- and 15-d denervated (Den) TA muscle. (D) Real-time PCR was used to quantify the temporal induction of Mgn, HDAC4, HDAC6, and MSE mRNAs after TA muscle denervation. Values are normalized to γ-actin and reported relative to innervated muscle RNA levels (0-h denervation). (E) Western blot analysis of denervation-dependent HDAC4 and Mgn protein induction. Proteins from innervated (Inn) or denervated TA muscles were assayed by Western blot analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Note the increased expression of HDAC4 and Mgn shortly after muscle denervation, whereas the MHC expression remains relatively constant.