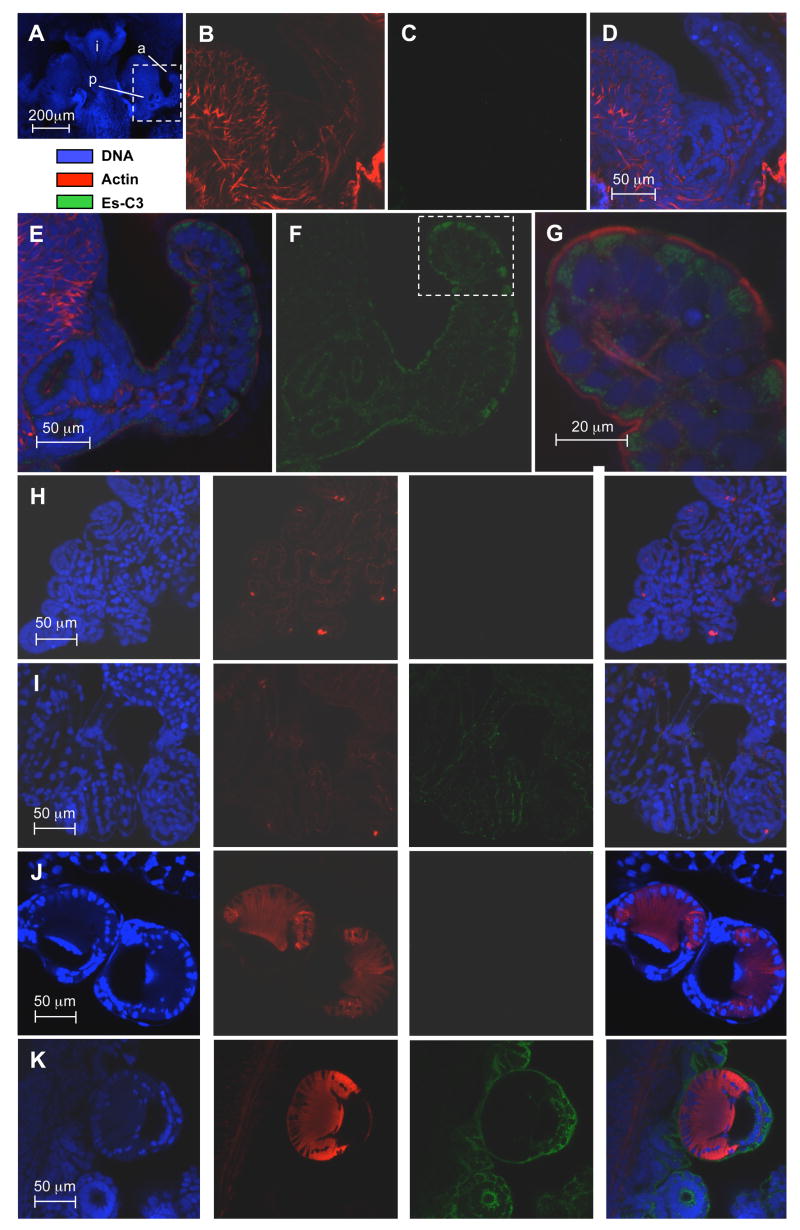
Fig 5.
Localization of Es-C3 in juvenile E. scolopes by confocal microscopy. (A) For orientation, the juvenile light organ, and adjacent tissues, labeled solely with the nuclear DNA stain TOTO-3 iodide (intestine, i). The area enclosed in the white box, a portion of one side of the organ including the anterior appendage (a) of the superficial ciliated field and the pore region (p) where symbionts enter, is magnified in panels B–G. (B–D) A representative preimmune control, demonstrating low cross reactivity against anti-Es-C3. (E–G) Light organ treated with anti-Es-C3 antibody conjugated with FITC. Antibody cross reactivity localized to the apical surface of the light organ epithelial cells. Panels and G are composite images of all three labels; panel F shows only the signal received from the fluorescein dye, revealing that Es-C3 appears to be present in discrete areas within the cells. (H, I) Labeling in gill epithelial; H panels, preimmune controls; I panels, anti-Es-C3. (J, K) Labeling of the arm suckers. J panels, preimmune controls; K panels, anti-Es-C3. In panels H–K, right most images are the composite of all three labels. In these other tissues, Es-C3 is also found in the cytoplasm of cells in a similar distribution to that found in the light organ epithelia. All images are representative of at least three separate replicate treatments.