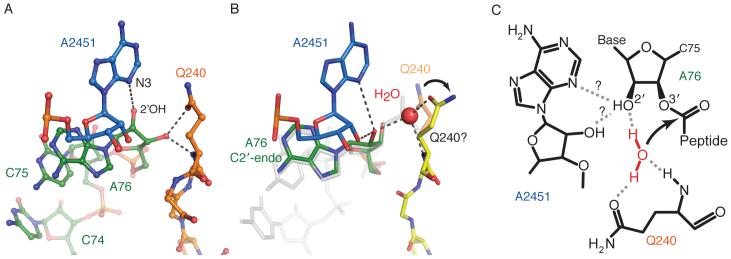
Fig. 4.
A model of the substrate complex suggesting the basis for catalysis. A. The interaction of Q240 of RF2 and A2451 of 23S RNA in the current structure. B. A proposed structure showing how a minor change in the orientation of Q240 would allow it to coordinate a water molecule (transparent orange versus yellow). In gray is a transition-state analog superposed on this structure [1VQ7, taken from (24)] that was used to place the putative water that would take part in nucleophilic attack on the ester bond. C. A schematic representation of how a network of interactions among the conserved Q240, the coordinated water molecule that is the attacking nucleophile, the ribose of A76 of P-site tRNA (in C2′-endo conformation) and A2451 would act to facilitate catalysis.