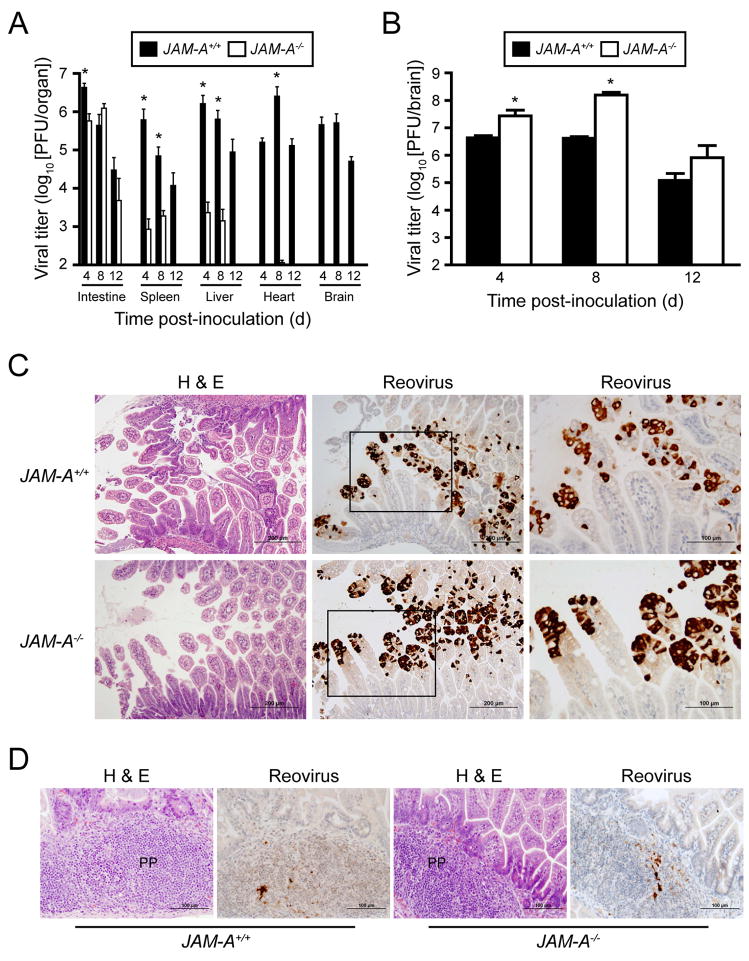
Figure 5. Reovirus T1L Is Incapable of Dissemination following Peroral Inoculation of JAM-A−/− Mice.
(A) Newborn JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− mice were inoculated perorally with 106 PFU T1L. At days 4, 8, and 12 after inoculation, mice were euthanized, organs were resected, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay. Results are expressed as mean viral titers for 6 animals for each time point. Error bars indicate SD. *, P < 0.005 by Student’s t test. When all values are less than the limit of detection (spleen, liver, heart, and brain in JAM-A−/− mice), a Student’s t test P value cannot be calculated.
(B) Newborn JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− mice were inoculated intracranially with 103 PFU T1L. At days 4, 8, and 12 after inoculation, mice were euthanized, brains were resected, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay. Results are expressed as mean viral titers for 6–11 animals for each time point. Error bars indicate SD. *, P < 0.005 by Student’s t test.
(C–D) Newborn JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− mice were inoculated perorally with 108 PFU T1L. At days 2 and 4 after inoculation, intestines of infected mice were resected and processed for histopathology. Consecutive sections were stained with H&E or polyclonal reovirus antiserum. Representative sections of intestinal villi at day 2 (C) and Peyer’s patches (PP) at day 4 (D) are shown. Boxes indicate areas of enlargement in the panels on the right and show villus epithelial cells.