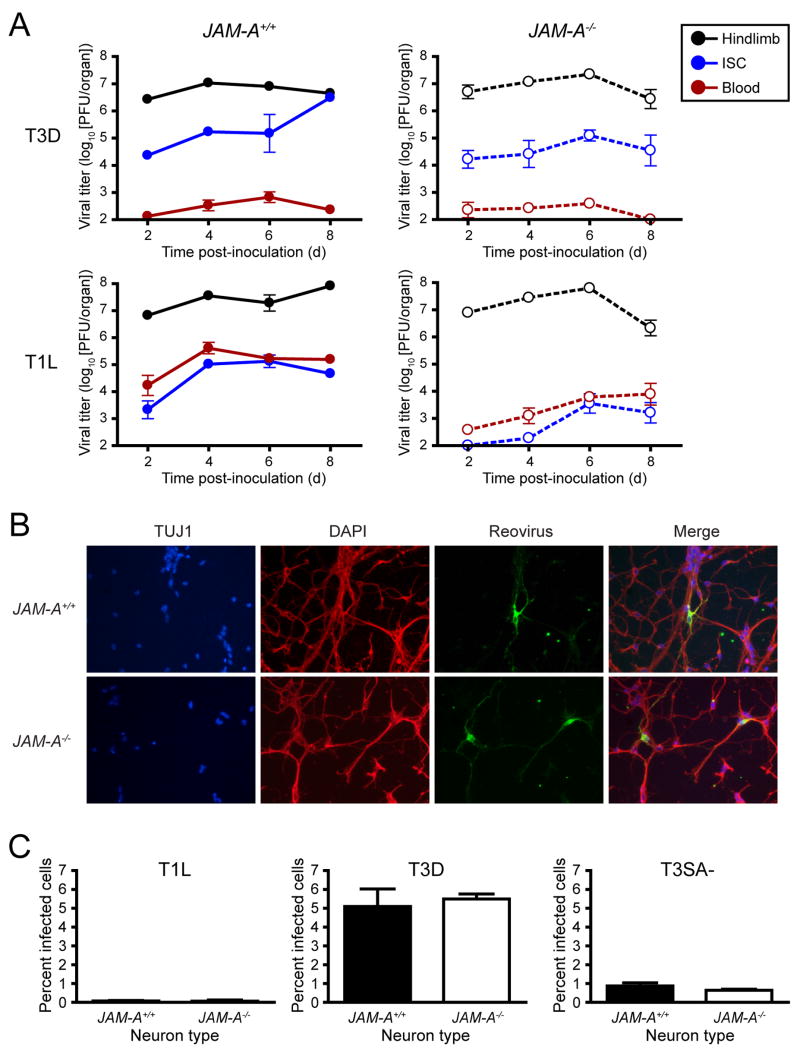
Figure 6. JAM-A Is Required for Hematogenous Spread of Reovirus.
(A) Newborn JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− mice were inoculated into the left hindlimb with 106 PFU of either T3D or T1L. At days 2, 4, 6, and 8 after inoculation, mice were euthanized, left hindlimb, blood, and inferior spinal cord (ISC), including the thoracic and lumbosacral cord segments, were resected, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay. Results are expressed as mean viral titers for 6 animals for each time point. Error bars indicate SD.
(B) Primary cortical cultures generated from E15 JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− embryos were cultured in vitro for 5 to 7 days, adsorbed with T3 reovirus at an MOI of 1000 PFU/cell, and incubated for 20 hr. Cells were stained with TUJ1 neural-specific marker to detect neurons (red), 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) to detect nuclei (blue), and polyclonal reovirus antiserum to detect reovirus antigen (green) and visualized using indirect immunofluorescence microscopy. Representative wells from triplicate experiments are shown.
(C) JAM-A+/+ and JAM-A−/− cortical cultures were cultured in vitro for 5 to 7 days and adsorbed with T1L, T3D, or T3SA- at an MOI of 1000 PFU/cell and incubated for 20 hr. The percentage of infected cells was quantified by dividing the number of neurons exhibiting reovirus staining by the total number of cell nuclei exhibiting DAPI staining in three fields of 400X view for triplicate experiments. Fields of view contained between 200 and 600 nuclei. Error bars indicate SD.