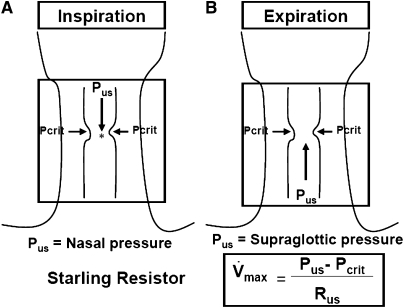
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration for the collapsible segment of upper airway during hypocapnic hypopnea as a Starling Resistor. In this model, flow is determined by the gradient between the upstream segment and critical closing pressure (Pcrit). During inspiration (A), when upstream pressure (Pus) (i.e., nasal pressure) is below the Pcrit, the collapsible segment is closed, and no flow occurs. During expiration (B), when Pus in the supraglottic area is below the Pcrit, the collapsible segment is closed, and no flow occurs. During hypocapnic hypopnea, expiratory flow is limited, correlating with the gradient between the supraglottic pressure and Pcrit. Hence, this pressure gradient is important determinant of pharyngeal narrowing. Rus = upstream resistance; Vmax = maximal flow. Asterisk represents the site of retropalatal pressure measurement.