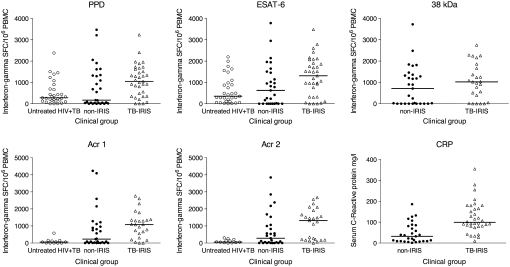
Figure 1.
Frequency of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen–specific IFN-γ spot-forming cells (SFCs) in HIV-infected patients with tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB–IRIS). Two comparator groups were patients with HIV-associated tuberculosis before treatment and not receiving combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) (untreated HIV+TB), and patients with treated HIV-associated TB also receiving cART for a similar duration to the patients with TB–IRIS (non-IRIS). The frequency of IFN-γ SFCs was higher in patients with TB–IRIS than in non-IRIS patients (P ≤ 0.03), with the exception of the response to 38-kD cell wall antigen. The frequency of IFN-γ SFCs was also higher in patients with TB–IRIS than in patients with untreated HIV+TB in every instance (P ≤ 0.004). By contrast, the frequency of IFN-γ SFCs did not differ between the non-IRIS and untreated HIV+TB groups in response to any antigen.