Figure 1.
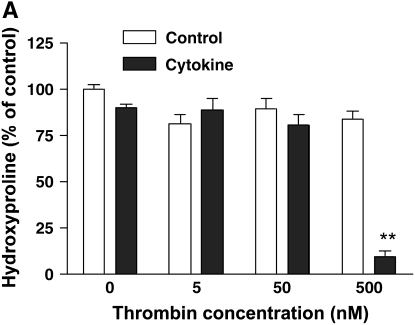
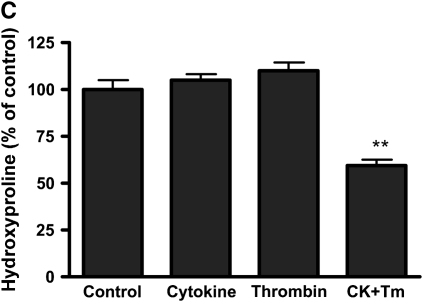
Effect of thrombin and cytokines on collagen gel degradation. (A) Cell-dependent effect. Gels containing HFL-1 fibroblasts (4.5 × 105/ml) were cast into serum-free DMEM containing different concentrations of thrombin (0 nM, 5 nM, 50 nM, and 500 nM) with or without cytokines (5 ng/ml TNF-α and 5 ng/ml IL-1β). The gels were cultured for 5 d and hydroxyproline content in the gels was determined. Vertical axis: hydroxyproline (% of Control). Horizontal axis: Thrombin (nM). Data presented are mean ± SEM for three separate experiments, each of which included triplicate gels for each condition. Open bars, SF-DMEM; filled bars, cytokines. The asterisks indicate P < 0.01 compared with control condition. (B) Effect of hirudin on collagen gel degradation. HFL-1 cells were cast into collagen gels and cultured for 5 d in the presence of cytokines (5 ng/ml of TNF-α and IL-1β) and thrombin (500 nM) with or without hirudin (5 U/ml). Gels were then harvested and hydroxyproline content was determined. Vertical axis: hydroxyproline (% of control). Horizontal axis: treatment. (C) Cell-independent effect. Gels containing HFL-1 fibroblasts (4.5 × 105/ml) were incubated with or without cytokines (5 ng/ml TNF-α and 5 ng/ml IL-1β) for 4 d. The conditioned medium was harvested. Gels without fibroblasts were cast and incubated in the conditioned medium with or without thrombin (500 nM). After 24 h, the hydroxyproline content in the gels was determined. Vertical axis: hydroxyproline content (% of Control). Horizontal axis: culture conditions. **P < 0.01 compared with control. CK, cytokines; Tm, thrombin.