Figure 2.
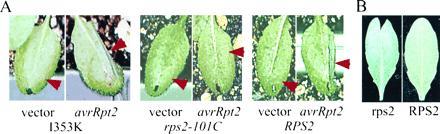
(A) The I353K RPS2 mutant gene can complement an rps2 mutant phenotype in transgenic plants. One-month old rps2-101C plants transformed with I353K (Left), with a rps2-101C mutant gene (Center), and with the RPS2 wild-type gene (Right) were inoculated at 0.5 × 107 colony-forming unit/ml with Psp 3121 carrying a vector control (pLAFR3) or carrying avrRpt2. Only one-half of each leaf (arrowhead) was inoculated. The photographs were taken 20 hr after inoculation. (B) Transient expression of avrRpt2 causes a reduction of cointroduced GUS gene expression in RPS2 plants. Leaves of RPS2 wild-type (Right) and rps2-101C mutant (Left) plants were bombarded with biolistics carrying the avrRpt2 and GUS constructs. After a 27-hr incubation, the leaves were histochemically stained for GUS activity. The cells that express GUS enzyme at a high level are visualized as blue dots on the leaves.
