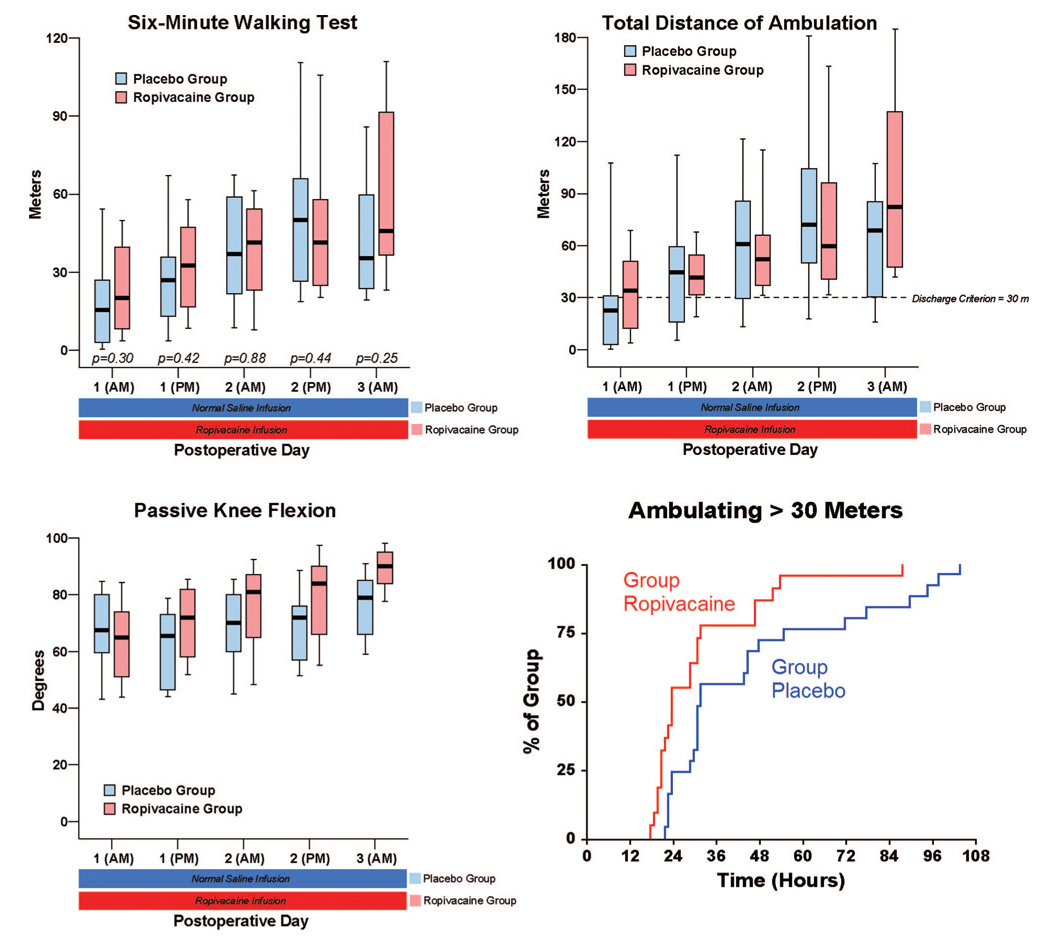
Fig. 3.
Effects of femoral perineural ropivacaine infusion on ambulation and passive knee flexion after tricompartment total knee arthroplasty. Kaplan-Meier estimates include the cumulative percentages of patients ambulating at least 30 m at each time point and subsequent time points. Other data are expressed as median (horizontal bar) with 25th–75th (box) and 10th–90th (whiskers) percentiles for patients randomly assigned to the ropivacaine group (perineural ropivacaine from surgery through postoperative day 4) or the placebo group (perineural ropivacaine from surgery through 06:00 postoperative day 1 followed by perineural normal saline through postoperative day 4). Because each comparison dilutes all other P values, we restricted our analysis to 11 comparisons among secondary endpoints. P values are provided where statistical comparisons were applied.