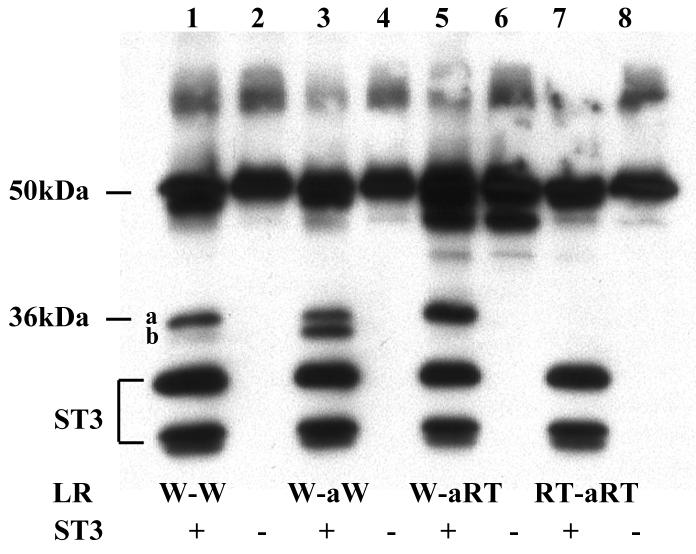
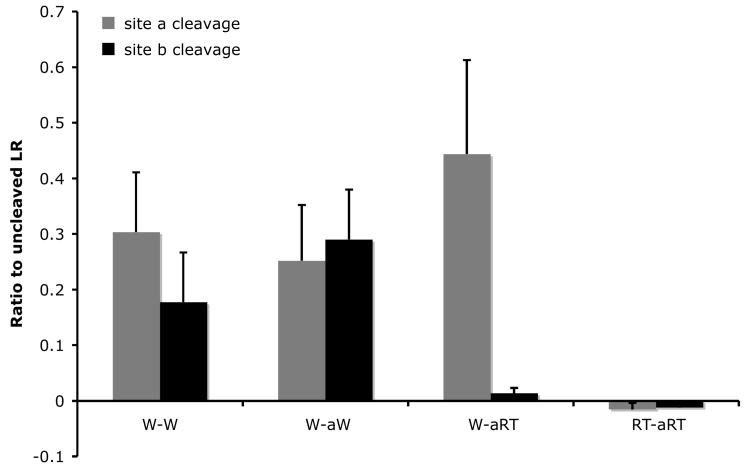
Fig. 5.
Substitution of the six amino acids at the cleavage site b with the corresponding ones at site a creates a cleavage site with site a characteristics. A. The 3 amino acids at either side of site b were replaced with the corresponding amino acids at site a to generate W-aW. RT mutations were then introduced into either one or both of the cleavage sites in W-aW to create the other mutants. His-tagged wild type LR and indicated mutants were synthesized by in vitro translation, purified, and digested with purified Xenopus ST3 catalytic domain. The samples were subjected to Western blotting with anti-Xenopus LR antibody. Note that RT mutation in the site b with the site a sequence completely blocked the cleavage by ST3 and RT mutation in site a failed to enhance the cleavage at this mutant site b (lane 7), in contrast to the corresponding mutants made from the wild type LR (Fig. 3, lane 9). The figure is a representative of 2 independent experiments with similar results.
B. Quantification of the data shown in A. Shown here is the average from 2 independent experiments.