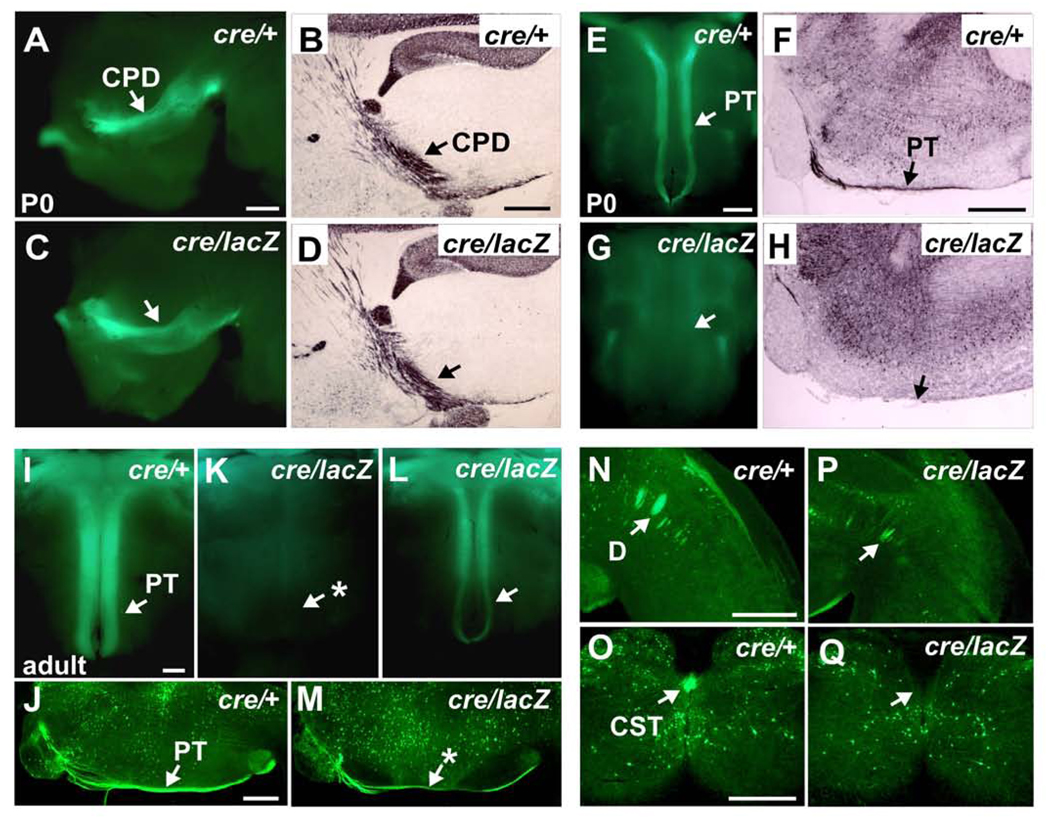
Figure 8. Loss of Bhlhb5 Function Causes Failure of Developmental Axon Targeting by Bhlhb5-expressing CSMN.
(A–Q) Genetic lineage axon tracing in Bhlhb5cre/+; Z/EG/+ heterozygote controls (cre/+) and Bhlhb5cre/lacZ; Z/EG/+ nulls (cre/lacZ).
(A–D) At P0, the cerebral peduncle appears normal in Bhlhb5-nulls via endogenous GFP fluorescence in side view of whole mount brains (A and C), and via GFP HRP-immunohistochemistry of sagittal brain sections (B and D).
(E–H) At P0, no Bhlhb5-expressing fibers are detected in the medullary pyramidal tract in Bhlhb5-nulls via endogenous GFP fluorescence in ventral views of whole mount brainstem (E and G), or via GFP immunohistochemistry of sagittal brainstem sections (F and H).
(I–M) In adults, very few Bhlhb5-expressing fibers are observed in the medullary pyramidal tracts of 10 of 17 Bhlhb5-nulls via endogenous GFP fluorescence (I and L). Bhlhb5-expressing fibers can be visualized in the other 7 (K) via GFP immunohistochemistry (J and M).
(N–Q) Bhlhb5-expressing fibers are observed in the medullary pyramidal decussation (N and P) but not in the ventral dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord (O and Q) in any Bhlhb5-nulls via GFP immunohistochemistry.
CPD, cerebral peduncle; PT, medullary pyramidal tract; D, decussation; CST, spinal segment of the corticospinal tract. P0 (controls n=4; Bhlhb5-nulls n=10); Adults (controls n=6; Bhlhb5-nulls n=17). Scale bars: 500 µm.