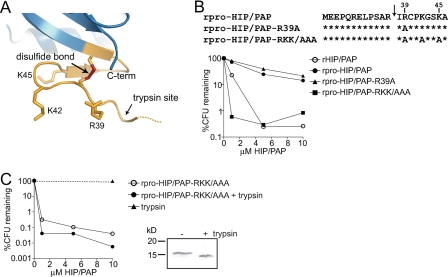
FIGURE 6.
HIP/PAP basic residues are essential for prosegment inhibition of antibacterial activity. A, orientation of Arg and Lys side chains near the HIP/PAP N-terminal trypsin site. The location of the trypsin cleavage site is indicated by an arrow. B, mutations of basic HIP/PAP residues yield active rpro-HIP/PAP. Comparison of antibacterial activity among rpro-HIP/PAP, rHIP/PAP, and rpro-HIP/PAP harboring the indicated mutations in basic residues. Antibacterial assays were performed as in Fig. 2. C, HIP/PAP basic residues (Arg39, Lys42, Lys45) are dispensable for antibacterial activity. Limited trypsin proteolysis was performed on rpro-HIP/PAP-RKK/AAA. SDS-PAGE analysis of the undigested and digested proteins is depicted. Digested and undigested proteins were analyzed for bactericidal activity as outlined in Fig. 2.