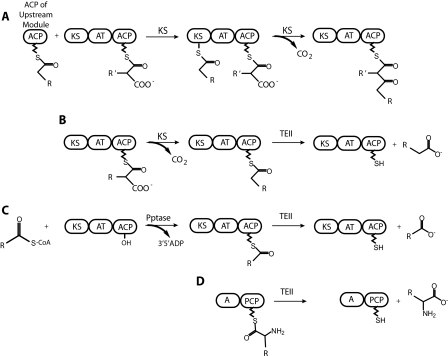
FIGURE 1.
Proposed functions of thioesterase II proteins. A, chain elongation by a PKS module. The chain elongation intermediate is transferred from the ACP of the upstream module to the ketosynthase (KS) domain. The acyltransferase (AT) domain transfers an acyl group building block from CoA to the ACP within the module. The KS domain catalyzes condensation of the new building block with the intermediate, releasing CO2. B, production of a decarboxylated acyl unit by the ketosynthase domain and the subsequent hydrolysis by a TEII. C, mispriming of a PKS by transfer of an acyl-phosphopantetheine arm by a promiscuous phosphopantetheinyl transferase (Pptase) and the subsequent hydrolysis by a TEII. D, hydrolysis of an amino acid derivative by a TEII from an NRPS module comprising an adenylation domain (A) and a peptide carrier protein (PCP) domain.