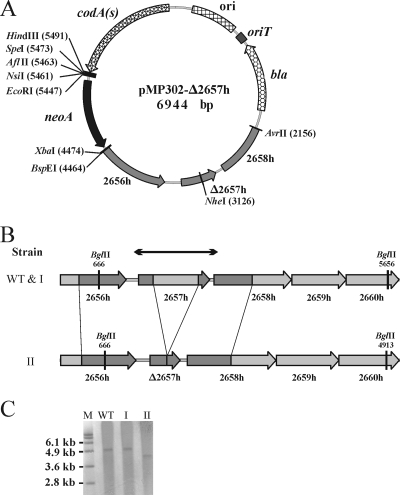
FIG. 2.
Inactivation of an S. lividans SCO2657 homolog gene (2657h) via replacement by an in-frame deletion. (A) Map of the pMP302 vector derivative (pMP302-Δ2657h) harboring PCR-amplified S. lividans genome fragments for homologous recombination. Positions of restriction sites are listed in parentheses. (B) Diagrams showing the wild-type (WT) genomic section of S. lividans and its configuration after the second crossing over. I, strain with a reversion to the wild-type configuration after two recombination events involving the same PCR-amplified fragment; II, strain with an in-frame deletion obtained by recombination events occurring alternatively in both amplified segments; 2656h to 2660h, S. lividans homologs of the respective S. coelicolor A3(2) genes; arrows, DNA fragment used as a probe in Southern blotting. Positions of restriction sites are given. (C) Southern blotting analysis of the 2657h gene area before (WT) and after (I or II) selection steps. Genomic DNA from the host strain (WT) and two PCR-preselected clones (I and II) resistant to 5FC was digested with BglII and analyzed by Southern blotting. M, molecular size markers.