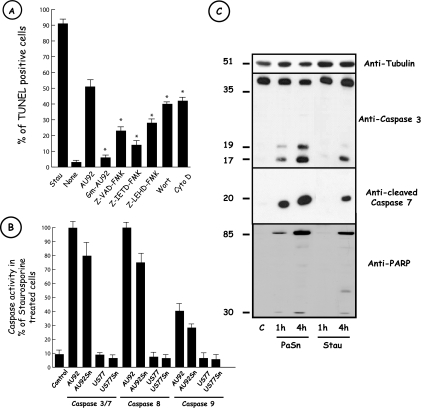
FIG. 3.
Apoptosis induced by AU92 requires caspase activity. (A) Effects of various inhibitors on AU92-induced THP-1 cell apoptosis. THP-1 cells were incubated with 20 μM Z-VAD-FMK, 10 μM Z-IETD-FMK, 10 μM Z-LEHD-FMK, 100 nM wortmannin (Wort), or 5 μg/ml cytochalasin D (Cyto D) 20 min before infection. Cells were infected with P. asymbiotica AU92 at an MOI of 100 for 6 h, and TUNEL labeling was performed. The different caspase and phagocytosis inhibitors significantly reduced the number of TUNEL-positive cells after P. asymbiotica AU92 treatment. Staurosporine (2.5 μM) (Stau) was used as an apoptosis positive control. None, no treatment. Results are means ± SD for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.01. (B) P. asymbiotica AU92 and P. asymbiotica AU92 Sn activated caspases in THP-1 cells. THP-1 cells were incubated with P. asymbiotica AU92, AU92 Sn, US77, US77 Sn, or staurosporine. Caspase activities were determined by the released of luminescent products following the manufacturer's protocol. Caspase activities are expressed as percentages of those in staurosporine-treated cells. Results are means ± SD for three independent experiments. (C) P. asymbiotica induces caspase-3/7 and PARP cleavage. After 1 or 4 h of incubation of THP-1 cells with P. asymbiotica AU92 or bacterial supernatant (PaSn), total protein extracts were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting with anti-caspase-3, anti-cleaved caspase-7, and anti-PARP antibodies. Native (around 35 kDa) and cleaved (around 20 kDa) forms of caspase-3, the cleaved form of caspase-7 (around 20 kDa), and PARP (around 85 kDa and 30 kDa) were already present after 1 h of incubation of THP-1 cells with PaSn. The same results were obtained with living but not with dead bacteria (data not shown). Staurosporine (2.5 μM) (Stau) was used as an apoptosis positive control. c, no treatment. Data are representative of three independent experiments.