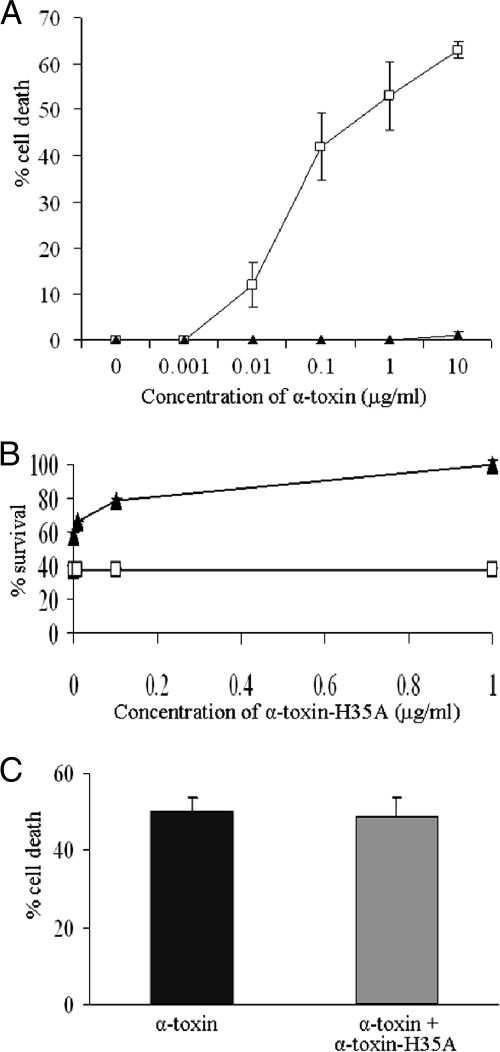
FIG. 2.
Effect of mutated H35A toxin on the capacity for alpha-toxin-induced cell death. (A) Alpha-toxin-H35A inhibits alpha-toxin-induced cell death. Monolayers of A549 cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were pretreated for 30 min with 1 μg/ml of alpha-toxin-H35A (solid triangles) or control (open squares) without any treatment before exposure to different concentrations of alpha-toxin. Cell viability was determined by measuring LDH release 16 h after the final treatment and is expressed as an average of data from at least three experiments ± standard deviations. (B) Efficacy of alpha-toxin-H35A in inhibition of alpha-toxin-induced cell death. Monolayers of A549 cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were exposed to different mixtures of toxins containing 10 μg/ml of alpha-toxin in the presence of different amounts of alpha-toxin-H35A (solid triangles) or without alpha-toxin-H35A (open squares). Cell viability was determined by measuring LDH release 16 h after the final treatment and is expressed as an average of data from at least three experiments ± standard deviations. (C) Impact of alpha-toxin-H35A on the progress of alpha-toxin-induced cell death. Monolayers of A549 cells (2 × 105 cells/well) were exposed to alpha-toxin (10 μg/ml) for 30 min before extra alpha-toxin-H35A (1 μg/ml) was added (gray bar). Cell viability was determined by measuring LDH release 16 h after the final treatment and is expressed as an average of data from at least three experiments ± standard deviations.