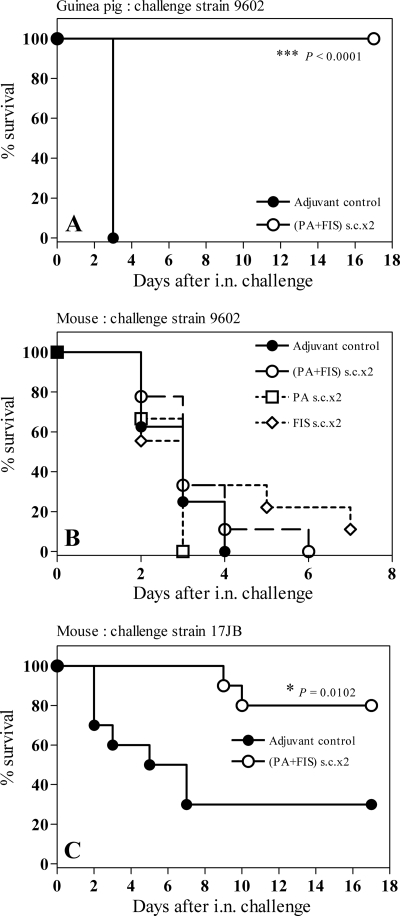
FIG. 1.
Efficacy of s.c. vaccination with PA-FIS in the guinea pig and mouse models of respiratory anthrax. (A) Guinea pigs were s.c. immunized twice with PA-FIS (s.c.×2; see Materials and Methods). Three weeks after the booster injection, all animals (six per group) were i.n. infected with 50 LD50 of B. anthracis 9602 spores; 2.6 × 106 spores were recovered from the lungs at time zero. The guinea pigs were observed for 17 days after exposure. The number of survivors in the PA-FIS group was significantly greater than that in the control group (***, P < 0.0001). (B and C) Mice were s.c. immunized twice with either PA-FIS, PA alone, or FIS alone (s.c.×2). Three weeks after the booster injection, all animals (10 per group) were either i.n. infected with 9 LD50 of B. anthracis 9602 spores and observed for 6 days after exposure (B) or i.n. infected with 8 LD50 of B. anthracis 17JB spores and observed for 17 days after exposure (C). The number of mice in the PA-FIS group surviving the 17JB challenge was significantly greater than that in the adjuvant control group (•) (*, P = 0.0102) (C).