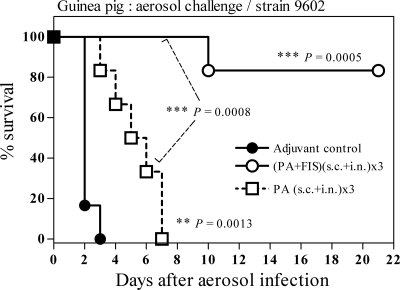
FIG. 5.
Efficacy of PA-FIS against aerosol challenge in the guinea pig model of inhalational anthrax. Guinea pigs were immunized with either PA-FIS or PA alone both s.c. and i.n., i.e., (s.c.+i.n.)×3. Three weeks after the second booster injection all animals (six per group) were exposed to a muzzle-only aerosol challenge with B. anthracis 9602 spores. An aqueous suspension containing 2.9 × 107 spores per ml was aerosolized. The actual inhaled dose was 2.7 × 105 spores, corresponding to approximately 75 LD50, as determined by bacterial counting in the lungs of two control animals at time zero. Guinea pigs were observed for 21 days after exposure. The number of guinea pigs in the PA-FIS group surviving the challenge was significantly higher than those in both the adjuvant control group (***, P = 0.0005) and the PA group (***, P = 0.0008). The number of survivors in the PA group was significantly higher than that in the adjuvant control group (**, P = 0.0013).