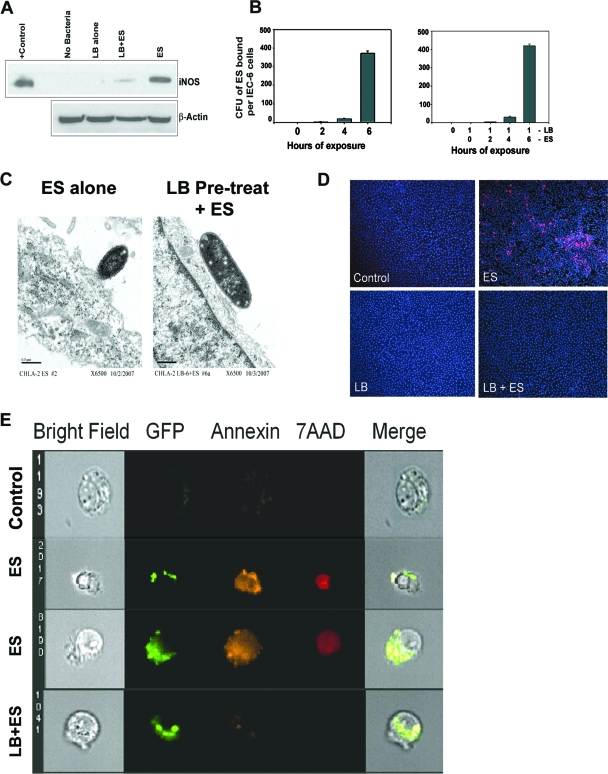
FIG. 2.
Pretreatment with L. bulgaricus prevents E. sakazakii-induced apoptosis in IEC-6 cells. (A) Total cell lysates of IEC-6 cells, either noninfected, infected with E. sakazakii (ES) or L. bulgaricus (LB), or pretreated with L. bulgaricus for 1 h followed by infection with E. sakazakii (LB+ES) were subjected to Western blotting with anti-iNOS or anti-β-actin antibody. A positive control for iNOS was also included in the blot. (B) Confluent monolayers of IEC-6 cells were infected with E. sakazakii for various periods and washed, and the number of bound E. sakazakii cells was determined as described in Materials and Methods. In separate experiments, IEC-6 cells were pretreated with L. bulgaricus for 1 h followed by E. sakazakii for the indicated periods. (C) IEC-6 cells infected with E. sakazakii or pretreated with L. bulgaricus for 1 h followed by E. sakazakii infection for 6 h were subjected to transmission electron microscopy. Magnification, ×6,500. (D) IEC-6 cells that were uninfected, infected with E. sakazakii, or pretreated with L. bulgaricus followed by E. sakazakii (LB+ES) for 6 h were subjected to TUNEL staining using an ApoTag kit. (E) IEC-6 cells were left uninfected (control), infected with GFP-labeled E. sakazakii alone (two panels of images are shown), or pretreated with L. bulgaricus for 1 followed by GFP-labeled E. sakazakii (LB+ES) for 4 h. The cells were stained with annexin V and 7-AAD as described in Materials and Methods and subjected to ImageStream analysis. The picture is representative of several cells screened for apoptosis.