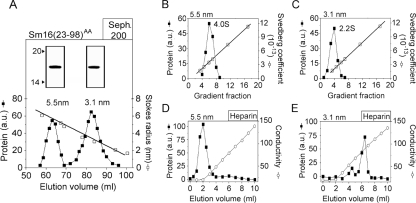
FIG. 3.
Identification of two oligomeric forms in a preparation of the C-terminally truncated Sm16(23-98)AA protein. (A) The Sm16(23-98)AA protein contains Ala substitutions for Ile-92 and Leu-93 to prevent aggregation. The metal ion affinity-purified protein was separated by Sephadex 200 gel filtration, and fractions were analyzed and quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. Open and filled symbols indicate the elution peaks of protein standards with known Stokes radii and Sm16(23-98)AA, respectively. The estimated Stokes radii of the two peaks are indicated. Peak fractions corresponding to Stokes radii of 5.5 and 3.1 nm, respectively, were pooled and analyzed by SDS-PAGE as described in the legend to Fig. 2A (insert). (B and C) Sedimentation properties of pooled peak fractions (insert in panel A) of Sm16(23-98)AA species with Stokes radii of 5.5 nm (panel B) and 3.1 nm (panel C) were analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 2C. (D and E) Heparin binding of pooled peak fractions (insert in panel A) of Sm16(23-98)AA species with Stokes radii of 5.5 nm (panel D) and 3.1 nm (panel E). Proteins diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (0.15 M NaCl) were passed over a column containing heparin coupled to Sepharose. Columns were eluted with a linear gradient of 0.15 to 1.0 M NaCl. Proteins in the fractions were analyzed and quantitated as described in the legend to Fig. 2B. The data plotted are representative of at least two independent analyses, and the experimental errors in the estimations of Stokes radii and sedimentation coefficients were <7%. a.u., arbitrary units; Seph, Sephadex. The values to the left of the inserts in panel A are molecular sizes in kilodaltons.