FIG. 4.
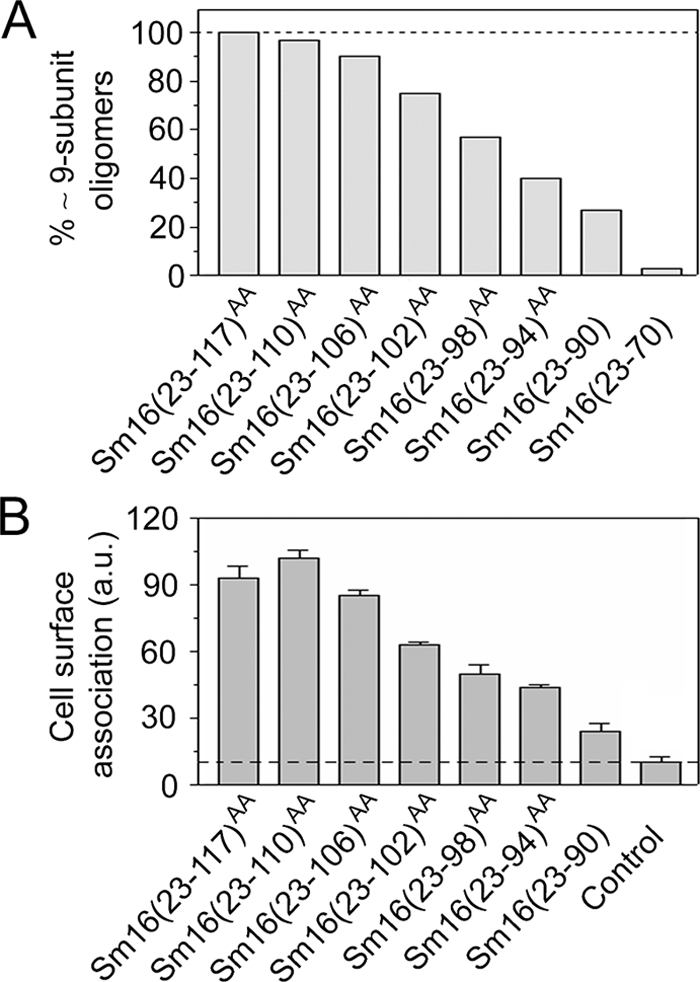
Importance of C-terminal regions for Sm16 oligomerization and cell surface binding. (A) The fraction of approximately nine-subunit oligomers, defined as a >4.5-nm Stokes radius, in metal ion affinity-purified preparations of the truncated Sm16 derivatives depicted in Fig. 1A was determined by Sephadex 200 gel filtration. Where indicated by the superscript AA, amino acid residues Ile-92 and Leu-93 were replaced with Ala to prevent protein aggregation. (B) Cell surface binding of approximately nine-subunit oligomers isolated by Sephadex 200 gel filtration of the indicated Sm16 derivative. The Sm16(23-70) protein does not show detectable affinity for cells (data not shown) but was not included in the present analysis since it does not form detectable amounts of approximately nine-subunit oligomers (panel A). Binding to live K562 erythroleukemia cells was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. Background binding, i.e., anti-Sm16 and fluorescein-conjugated swine anti-rabbit immunoglobulin, was ∼12% (dotted line). The presented data are representative of at least three independent experiments. a.u., arbitrary units.
