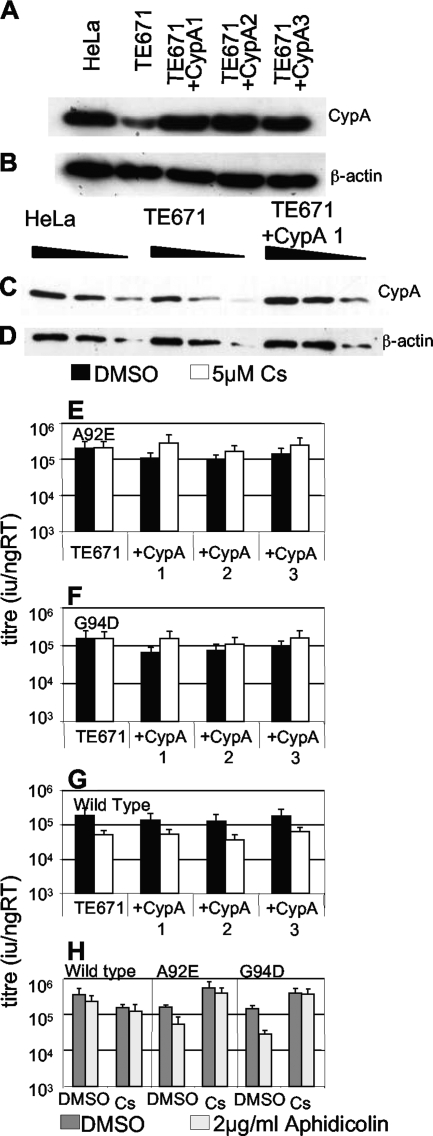
FIG. 2.
Overexpression of CypA in TE671 causes restriction of HIV-1 CA mutants. HeLa cells, parental TE671 cells, and three clones of TE671 transduced with a lentiviral CypA expression vector were analyzed by Western blotting for CypA expression (A and C) or β-actin as a loading control (B and D). Samples were equalized by assay of protein content (Bradford assay). Threefold serial dilutions of samples were loaded in panels C and D. Parental TE671 cells or three CypA-overexpressing TE671 clones were infected with A92E (E), G94D (F), or wild-type (G) HIV-1 GFP, in the presence (white bars) or absence (black bars) of 5 μM Cs. (H) Titers of wild-type, A92E, or G94D HIV-1 GFP were determined on TE671 cells overexpressing CypA (clone 1) in the presence (light gray bars) or absence (dark gray bars) of aphidicolin or the presence or absence of Cs (as shown). The cells were analyzed for infection by fluorescence-activated cell sorting 48 h later, and infectious titers were calculated. Titers are expressed as infectious units per nanogram reverse transcriptase, and errors are standard deviations of titers determined at three doses. The data are representative of two experiments using independent virus preparations. RT, reverse transcriptase; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.