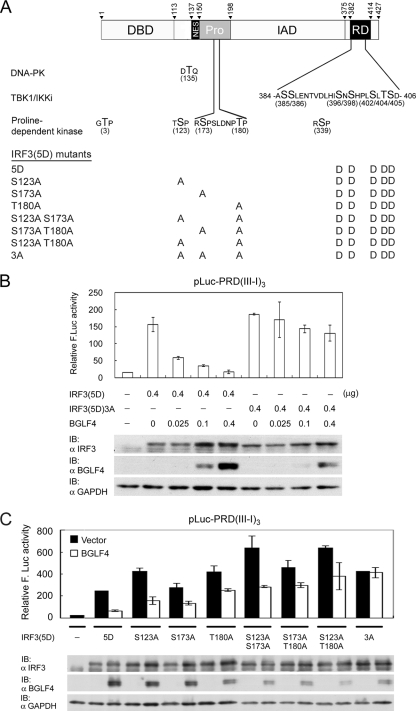
FIG. 7.
Ser123, Ser173, and Thr180 of IRF3 contribute additively to BGLF4-mediated suppression of IRF3(5D) in a transient reporter assay. (A) Summary of currently identified phosphorylation sites on IRF3 and IRF3(5D)-based mutants used in this study. Thr135 is the phosphorylation site of DNA-PK (37), and the seven phosphorylation sites in the response domain (RD) can be phosphorylated by TBK1 or IKKi (14, 19, 53, 63, 65). The proline-dependent phosphorylation sites are Thr3, Ser123, Ser173, Thr180, and Ser339. Ser339 is phosphorylated by unidentified cellular kinase and contributes to Pin-mediated IRF3 degradation (60). Mutants generated for mapping residues responsible for BGLF4-mediated suppression are listed. NES, nuclear export signal. (B) A reporter assay was performed by cotransfecting plasmids expressing constitutively active IRF3(5D) or IRF3(5D)3A and increasing amounts of BGLF4 with reporter plasmid pLuc-PRD(III-I)3 and the GFP control into HeLa cells. At 24 h posttransfection, luciferase activities were measured and normalized to GFP activity. IB, immunoblot. (C) A reporter assay was performed by cotransfecting IRF3(5D), IRF3(5D)S123A, IRF3(5D)S173A, IRF3(5D)T180A, IRF3(5D)S123A S173A, IRF3(5D)S173A T180A, or IRF3(5D)S123A S173A T180A [IRF3(5D)3A] in the presence of BGLF4 or vector with the reporter plasmid into HeLa cells and assayed as described above (B). In all experiments, results are means ± SD from two separate transfections. Data are representative of two independent experiments.