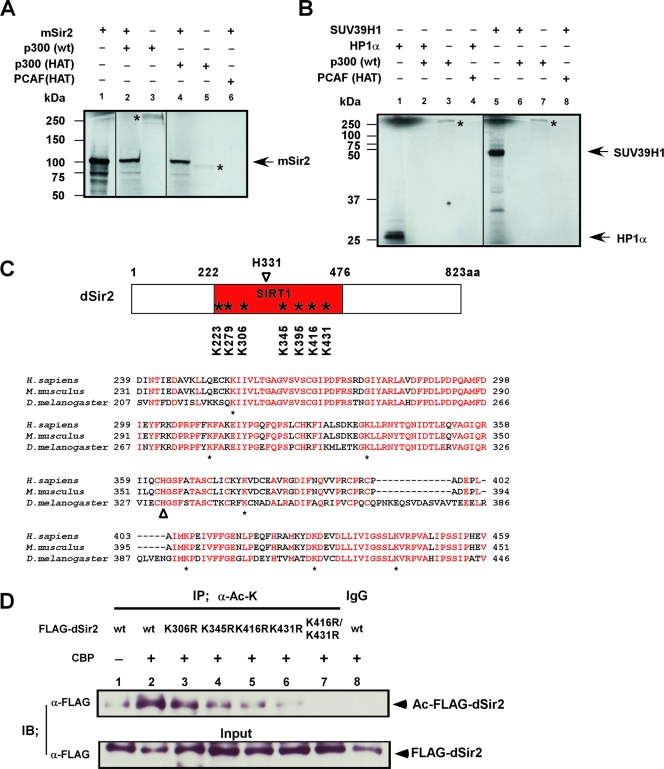
FIG. 6.
dSir2 is acetylated by dCBP in vivo and in vitro at its conserved HDAC catalytic core region. (A and B) dCBP human homologue (p300) or p300/CBP HAT acetylates Sir2 in vitro. The p300, GST-P300/CBP HAT, and GST-PCAF HAT proteins were subjected to in vitro acetylation assays with in vitro-synthesized substrate proteins, including mSir2, human HP1α, and SUV39H1. Reaction products were analyzed by autoradiography (14C). The autoacetylated p300 or p300/CBP HAT is indicated with a star. Fractions of 35S-labeled in vitro-synthesized substrate proteins (2.5%) were used as the input (panel A, lane 1; panel B, lanes 1 and 5). (C) (Upper panel) Schematic representation of Sir2 orthologues in Drosophila flies (dSir2); the conserved lysine sites at its catalytic core regions (SIRT1 domain) are indicated with stars. H331 is a well-defined catalytic site of dSir2 (open arrowhead). (Lower panel) Sequence alignment of the conserved core region with the SIRT domains from several species as indicated. Conserved residues with 100% identity are indicated with red characters. Below the alignment, conserved lysine (K) residues are labeled (stars); histidine (H) residues (marked with an open arrowhead) represent a well-defined catalytic site of Sir2. (D) 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-dSir2 wt or a series of FLAG-dSir2 mutation expression plasmids together with CBP expression vector as indicated. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-acetylated lysine antibody (α-Ac-K [mouse monoclonal]) or with control preimmune mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG). Precipitated proteins and fractions (5%) of the input cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-FLAG antibody.