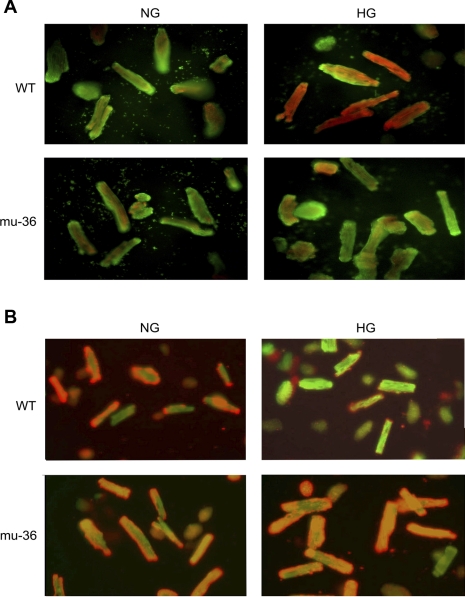
Fig. 3.
A: p66ShcA-dependent regulation of HG-induced oxidant stress. ARVMs and mu-36 ARVMs were maintained in SFM containing 5 mM (NG) or 25 mM (HG) glucose for 16 h. Cells were loaded Redox Sensor Red CC-1 and the mitochondrial-specific dye MitoTracker green FM. At HG, ARVMs show reddish-orange fluorescent signal due to colocalization of oxidized red CC-1 and MitoTracker green in mitochondria. B: Mu-36 p66ShcA inhibits HG-induced collapse of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. ARVMs and mu-36 ARVMs were maintained in SFM containing 5 mM (NG) or 25 mM (HG) glucose for 16 h. Cells were loaded with the fluorescent probe JC-1 that exhibits potential dependent accumulation in mitochondria. Under control conditions (5 mM glucose), ARVMs and mu-36 ARVMs showed punctate red stain due to JC-1 accumulation in mitochondria (J-aggregates). At HG, mitochondria of ARVMs depolarize, indicated by release of JC-1 into cytoplasm and shift from red to green fluorescence.