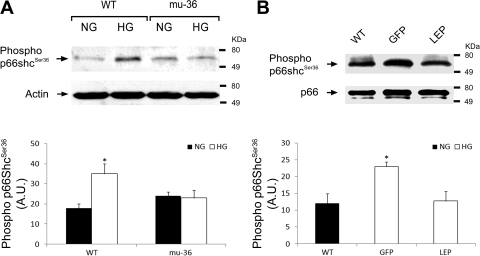
Fig. 5.
Mu-36 and leptin inhibit phospho-Ser36 in p66ShcA. A, top: representative Western blot analysis showing phosphorylation status of Ser36 in lysates prepared from ARVMs. Protein extracts from WT ARVMs and ARVMs transduced with GFP and mu-36 were separated by PAGE and nitrocellulose blots probed with mouse monoclonal anti-phospho-serine antibody that recognizes the 66 kDa form of Shc phosphorylated at Ser36. A, bottom: densitometric analysis for phospho-Ser36 expression. Data represent 4 independent experiments: means ± SD and *P ≤ 0.05. B, top: representative Western blot analysis showing phosphorylation status of Ser36 in lysates prepared from hearts of WT and Akita mice expressing rAAV-GFP (GFP) or rAAV-Lep (LEP). Protein extracts from WT, GFP, and LEP groups were separated by PAGE and nitrocellulose blots probed with mouse monoclonal anti-phospho-serine antibody as in A. B, bottom: densitometric analysis for phospho-Ser36. Data represent 3 to 4 independent experiments: means ± SD and *P ≤ 0.05.