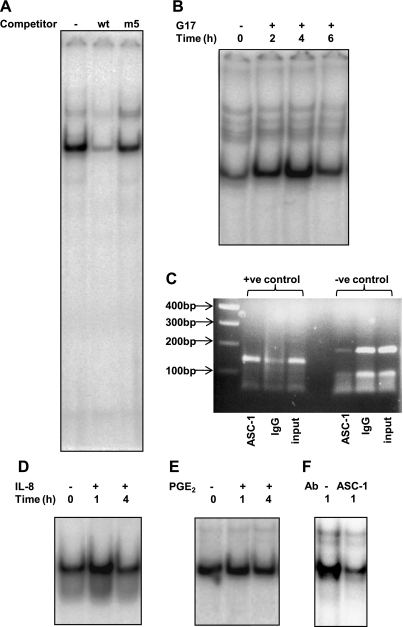
Fig. 5.
Analysis of the −81 to −59 region of the PAI-2 promoter. A: wt and mutant ds oligonucleotides (100× excess) were used to compete with radiolabeled wt probe binding to nuclear extracts from gastrin-stimulated AGS-GR cells. B: time course of wt probe binding to nuclear extracts from gastrin-stimulated AGS-GR cells. Lane 1: unstimulated cells; lanes 2-4: cells stimulated with G17 (1 nM) for times indicated. Representative data from 3 replicate experiments. C: PCR analysis of ChIP assay. Lane 1, 100-bp marker. Lane 2, positive control primers (143-bp amplicon) with ASC-1 immunoprecipitated DNA as template. Lane 3, positive control primers with IgG immunoprecipitated DNA as template. Lane 4, positive control primers with unprecipitated input DNA as template. Lanes 5-7, templates as for lanes 2-4 but with negative control primers (186-bp amplicon). D: time course of wt probe binding to nuclear extracts from gastrin-stimulated AGS-GR cells. Lane 1, unstimulated cells; lanes 2-3, cells stimulated with IL-8 (125 ng/ml) for times indicated. E: time course of wt probe binding to nuclear extracts from gastrin-stimulated AGS-GR cells. Lane 1: unstimulated cells; lanes 2-3: cells stimulated with PGE-2 (28 μM) for the times indicated. F: effects of ASC-1 antibody on wt probe binding to nuclear extracts from G17-stimulated AGS-GR cells. Lane 1, control rabbit IgG; lane 2, ASC-1 antibody.