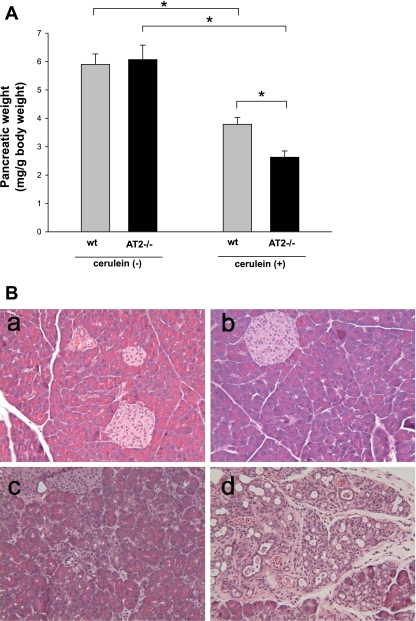
Fig. 3.
Severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis after repetitive episodes of acute pancreatitis. Mice were subjected to 3 episodes of acute pancreatitis (6 cerulein treatments per day every other day for 3 days) and euthanized 3 days after the last treatment. A: pancreatic weight relative to total body weight. Note the decrease in pancreatic weight of cerulein-treated AT2−/− mice compared with cerulein-treated WT mice (8 mice per group), *P < 0.001. B: histological changes in the pancreas of WT and AT2−/− mice after repetitive episodes of acute pancreatitis (6 mice per group, hematoxylin and eosin stain, original magnification ×200). Control pancreas from WT (a) and AT2−/− mice (b) after control saline treatment. Pancreas from cerulein-treated WT (c) and cerulein-treated AT2−/− (d) mice. Note more severe morphological alterations such as disruption of acinar cell architecture and inflammatory cell infiltration in cerulein-treated AT2−/− mice (d) compared with cerulein-treated WT mice (c).