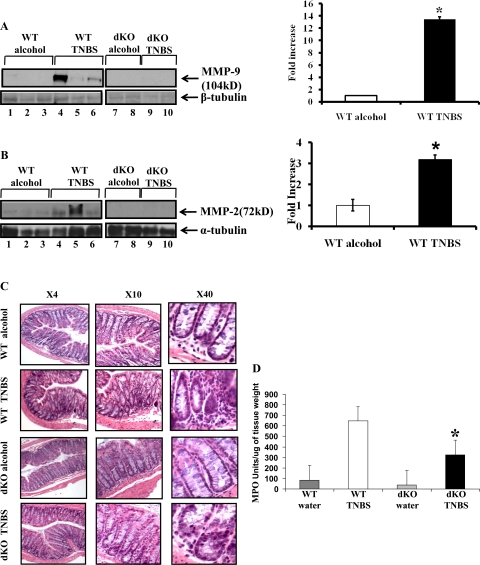
Fig. 4.
MMP-2−/−/MMP-9−/− dKO mice are resistant to trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. WT C57/B6 and MMP-2−/−/MMP-9−/− dKO mice 8 wk old were weighed and treated with or without TNBS for 48 h. Mice were euthanized, and colon was processed for Western blot and histology. A and B: representative Western blots of protein from the colon of WT mice given vehicle (lanes 1–3) or TNBS (lanes 4–6) and MMP-2−/−/MMP-9−/− dKO mice given vehicle (lanes 7–8) or TNBS (lanes 9–10). Western blot was quantified by scanning densitometry and represented in adjacent graphs as the fold increase of MMP-9/β-tubulin (A) or MMP-2/α-tubulin (B) in WT mice treated with TNBS compared with WT mice treated with vehicle. Values are representative of 3 individual experiments, means ± SE; n = 10. Disease severity was assessed and expressed in terms of histological score. C: representative photomicrographs from 2 individual experiments; n = 10 for TNBS group and n = 10 for control group with magnifications ×4, ×10, and ×40. Colon were snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and myeloperoxidase activity was measured (D) as an index of neutrophil infiltration into the injured tissue. Each bar represents mean ± SE; n = 10 animals for each group. *P < 0.05.